Ontogenetic and interpopulation differences in otolith shape of the European perch (Perca fluviatilis)
Abstract
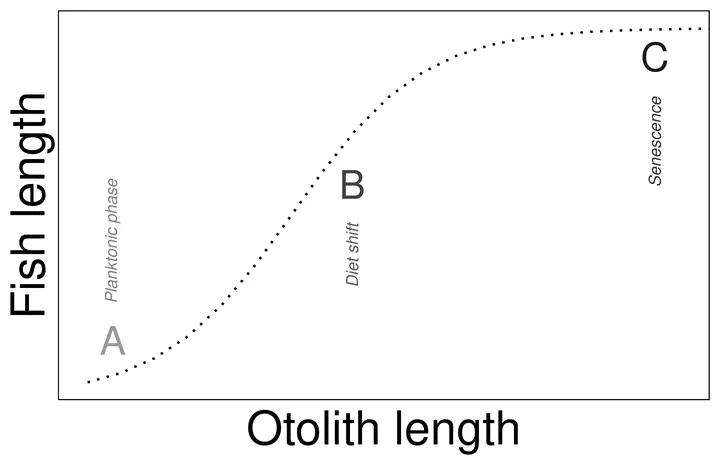
Fish otoliths are conservative structures that are widely used on fishery science for multiple purposes. Despite its relevance in the research field, little is known about the ontogeny and inter-population effects on the otolith of freshwater fish. In this study we used otoliths from 1800 European perch (Perca fluviatilis) individuals from 9 different populations to analyze the ontogenetic and inter-population differences on the otolith shape using six morphometric indices. The relationship between fish and otolith length was fitted using three different regression models (linear, power and logistic) to identify the best allometric relationship. Our results show that there are strong ontogenetic and interpopulation differences in P. fluviatilis otolith shapes. We also show that the relationship between the fish and otolith length follows a logistic curve. The ontogenetic differences on otolith shape might be related to extrinsic factors (diet shift and intra and interspecific competition) in each ecosystem, given that the reservoirs are different and no clear pattern on the otolith shapes can be distinguished among populations. Our results imply that the available back-calculation models may not always provide accurate estimates of P. fluviatilis length and that a model that takes into account the real allometric relationship for the species can improve the fish length estimations of back-calculated fish lengths for the European perch.