Publications

As a significant piscivorous predator, the pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) plays a critical role in regulating aquatic ecosystems. Understanding its size-related feeding behaviour is thus vital for assessing its impact. To evaluate its role in the ecosystem, stomach content analysis provides useful insights into predator–prey dynamics. This study investigated the stomach content and dietary patterns of pikeperch in the Lipno Reservoir, Czech Republic, across two distinct time periods: the 1966–1970 (19’s) and the 2010–2022 (20’s). We analysed the stomach contents of 875 pikeperch specimens and revealed a notable shift in diet composition over time. The results demonstrated a significant decrease in overall prey consumption and a marked increase in the proportion of cyprinids in the diet, whereas the percentages of perch (Perca fluviatilis) and ruffe (Gymnocephalus cernua) decreased. Cannibalism was observed in the 20’s dataset, suggesting a reduction in prey abundance in the reservoir or a shift in community structure. The predator–prey length ratio (PPR) decreased as pikeperch grew larger. The PPR values in Lipno Reservoir were lower than those reported in other studies, indicating potentially slower growth rates in this fish. Although percids were the main prey of pikeperch, the electivity index showed positive values only for pikeperch as the prey. Overall, this study highlights long-term changes in pikeperch diets, both in the numbers and species of prey and in PPR.

Intraspecific competition is a fundamental selective force in animals, leading to various specializations that influence ecological interactions. Diet composition and trophic position at the early life stages substantially influence fish growth, survival, and recruitment success. Yet, most studies focus disproportionately on adult stages, leaving critical knowledge gaps in our understanding of early life history. To address this, we used young of the year (YOY) pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) as a model species and investigated the intraspecific interaction and degree of trophic partitioning between three intra-annual cohorts (extremely small (ES), ordinary and piscivorous YOYs) using stable isotope (SI) and gut content analysis (GCA). Analysis of SI metrics unveiled that an ontogenetic diet shift was linked to increasing body size, leading to significant trophic niche variation among intra-annual cohorts. The piscivorous cohort occupied the highest trophic position, followed by the ordinary and ES cohorts. There was no overlap in the isotopic niche between the intra-annual cohorts, considering the 40% standard ellipse area. The GCA showed two distinct feeding patterns: the ES cohort exclusively consumed zooplankton, while the ordinary cohort had a more diverse diet, feeding on zooplankton and benthic macroinvertebrates. The piscivorous cohort (≥ 80 mm) predominantly fed on their conspecifics and YOY perch (Perca fluviatilis). Our study demonstrates that YOY pikeperch intra-annual cohorts exhibit a broad size range and unique ontogenetic feeding patterns, with vital implications for population dynamics and ecological interactions. These differences are likely due to different hatching dates, environmental factors, and individual ability to become predatory. Furthermore, this work emphasizes the need for comparative studies to better understand trophic dynamics and uncover the ecological factors shaping the early life stages of fish.

European Biodiversity Research Infrastructures (BioRIs) play a central role in addressing the complex challenges in biodiversity research, scientific collaboration across disciplines and national boundaries, as well as informing the public and policy-makers about the status and challenges of the European biodiversity. Our study focuses on the communication and coordination amongst BioRIs and revealed important fragmentation in communication strategies both within and across the key European BioRIs — including DiSSCo (Distributed System of Scientific Collections), eLTER (Integrated European Long-Term Ecosystem Research), GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) and LifeWatch ERIC. This fragmentation manifests in uneven geographical representation, inconsistent communication practices and limited data and service cohesion, ultimately impeding collaboration and the efficient use of resources. While some initiatives to tackle this issue demonstrate the potential for harmonisation, the the broader systemic challenges still persist. We argue that overcoming these barriers will require the development of standardised communication frameworks, more equitable distribution of infrastructures and deeper understanding of domain-specific differences that currently hinder the interoperability. Our study demonstrates the urgent need for coordinated efforts to integrate European BioRIs into a more coherent and accessible research ecosystem capable of addressing the biodiversity challenges of the 21st-century.

Large language models (LLMs) are becoming an integral part of our daily work. In the field of ecology, LLMs are already being applied to a wide range of tasks, such as extracting georeferenced data or taxonomic entities from unstructured texts, information synthesis, coding, and teaching. Further development and increased use of LLMs in ecology, as in science in general, is likely to intensify and accelerate the process of research and increase publication output—thus pressuring scientists to keep up with the elevated pace, which in turn creates a feedback loop by promoting even greater LLM use. However, this all comes at a cost. While not directly borne by end users, aside from occasional response delays, LLMs require considerable computational power and are energy-demanding during both their initial training phase and their subsequent operational use. Furthermore, partly externalized energy costs are linked to intensive searching and processing of discovered sources as part of Deep Research. Currently, it remains challenging to estimate the total energy costs of LLMs, largely due to limited transparency from their companies of origin.
The legacy data mobilization for eLTER standard observations (SOs) initiative was launched in November 2024. This initiative aimed to map and ingest untapped data resources of six selected SOs across the continent into the eLTER Digital Asset Registry (eLTER DAR). The data mobilization also focused on profiling the data providers, their preferences, skills, and experiences when dealing with heterogeneous environmental data. To do so, all data providers had to fill out an Expression of Interest Form (EIF) detailing the data to be mobilized as well as their preferred practices and tools when managing datasets, and the current solutions employed for data storage. A total of 54 unique applications were received, with data providers from 13 different countries. Data providers were willing to mobilize data mostly from SOs related to meteorology, vegetation composition, and soil inventory geological characterization, which were present in more than 65% of the applications, while the SOs related to the aquatic habitats were offered less often, with surface water algae (20% of the applications), and the physical chemical characteristics standing waters (27% of the applications). Analysis of the collected responses revealed that data contributors have a diverse range of experience levels, indicating a mixture of novice and seasoned contributors within the community. Most of the applicants do not have experience providing data to Research Infrastructures, with a few having experience with other RIs (e.g., ICOS and ICP Integrated Monitoring). The preferred tools for data management did not vary much among applicants, with most of the data providers relying on tabular data processing on Excel. Our findings highlight the necessity for tailored support to data providers and the need to develop flexible data ingestion tools to ingest eLTER data. The findings emphasize the importance of understanding the diverse experiences of data contributors and the necessity of developing user-friendly tools and resources that take account of their needs and provide training across the eLTER community. The insights gained from this study can serve as a foundation for future initiatives aimed at improving data management practices and enhancing the overall quality of ecosystem research across European RIs.
The Biodiversity Digital Twin (BioDT) project aims to develop a comprehensive digital representation of biodiversity, focusing primarily on terrestrial ecosystems. Through a series of prototype Digital Twins (pDTs), the project seeks to empower citizens, researchers, and policymakers to interact with complex environmental data in real-time. This work presents a case study of two pDTs developed within the BioDT initiative: the Invasive Alien Species (IAS) pDT and the Real-time Bird Monitoring (RTBM) pDT. These prototypes integrate a variety of environmental datasets, including climate data and species occurrence information, to model and simulate biodiversity patterns under different stressors and scenarios. The web applications designed for these pDTs leverage the power of R Shiny, a popular tool for building interactive web-based data visualizations. One of the primary challenges in developing these applications is handling the large, complex datasets while ensuring the user experience remains fluid and responsive. This requires an optimized data streaming system that can handle the intricate layers of data without overloading the web application’s performance. Efficient design strategies for real-time data integration are therefore crucial for achieving smooth interaction with the environmental data, ensuring users can explore and understand biodiversity dynamics across varying spatial and temporal scales. While the full impact of these applications on public engagement and decision-making is still under development, the goal is to facilitate a deeper understanding of how stressors such as climate change or invasive species affect biodiversity. The web applications will empower citizens to explore data on species distribution and gain insights into how different environmental scenarios can shape the future of biodiversity across the continent. By providing accessible, interactive tools, the BioDT initiative aims to support informed decision-making processes related to biodiversity conservation and environmental policy.
In an era of unprecedented environmental change, the need for long-term, integrated ecosystem research has never been more urgent. The first eLTER Science Conference brings together a vibrant community of researchers, site and platform coordinators, and visionaries dedicated to understanding and safeguarding the complex systems that sustain life on Earth. This proceeding includes all contributions to the first eLTER Science Conference in June 2025 in Tampere, Finland. The Conference is a pivotal moment in our shared journey toward deeper understanding, collaboration, and stewardship of our planet’s complex socio-ecological systems. It marks an important milestone in the scientific work towards the Whole Systems Approach that is the unique foundation of the eLTER RI, addressing the Earth system at different spatial and temporal scales in order to answer many of the burning scientific and societal questions of our time. In the Anthropocene, environmental research is ever more challenged to develop a holistic approach for understanding the compounded impacts of the multiple stressors on our ecosystems, including, e.g., climate change, biodiversity loss, soil degradation, pollution, and unsustainable resource use. No scientific community can address these challenges in isolation from others. Therefore, the eLTER Science Conference is a unique opportunity to hear and see how different communities and disciplines gather forces to study not only the different spheres (geo-, hydro-, bio-, atmo-, and socio-sphere), but especially the linkages amongst them on the habitable skin of the Earth. The high-level scientific and social programme of the Conference encourages diversity of approaches, exchange between generations of scientists, and inclusivity in the spirit of promoting inter- and trans-disciplinarity. The presentations highlight the key elements of eLTER’s vision: advancing integrated, long-term environmental research, promoting interdisciplinary collaboration, and supporting policy-relevant science for sustainability. The workshops offer a chance for hands-on engagement with various practical subjects while also exploring themes through artistic perspectives. The Conference week is composed of high-level keynote lectures, oral and poster sessions, inspirational exhibitions, workshops, and field trips, relevant for researchers from Europe and globally. The transdisciplinary dialogue is forming an important, cross-cutting element to the Conference program. Altogether 335 participants from 44 countries and 226 institutions will contribute their latest findings to the programme. The 25 prominent Keynotes will address their own research themes in a broad and comprehensive manner. Early career researchers (83) ensure fresh perspectives and energy to continue the ongoing renewal of the scientific enterprise. Interestingly, a common thread runs through many of the sessions: the word ‘Integration’ features in the titles of seven of them. This highlights a strong, shared ambition among participants to deepen collaboration not just within their own disciplines, but across the wider research landscape. It underscores a collective push toward developing harmonised methods and tools that can support more impactful, high-quality science. At the same time, it sends a clear message to the broader environmental science community: eLTER is open for collaboration and eager to connect. Beyond the rich scientific agenda, the eLTER Science Conference offers a diverse and engaging social programme, including Conference dinner on a charming Viikinsaari island and four guided excursions, each offering a unique perspective on Finland’s diverse ecosystems and long-term ecological research initiatives, and providing participants with immersive experiences into Finland’s ecological research and conservation efforts. The Scientific Committee ensured the high-level scientific content of the Conference. The Organising Committee was led by Jaana Bäck and Jerome Gaillardet, and included Paulina Rajewicz, Nina Hobbhahn, Alexandra Tzvetkova, and Michael Mirtl; in addition, Benat Olascoaga Gracia, Allan Souza, Janne Korhonen, and Syed Ashraful Alam and the 12 conference assistants contributed to making the Conference a success. With this Proceedings, we welcome all authors and other attendees to the first eLTER Science Conference, a landmark event in shaping the future of integrated ecosystem, critical zone, and socio-ecological research across Europe and beyond. We thank all contributors and participants for their valuable insights and commitment, and we look forward to continuing this journey — united in eLTER’s vision for a more sustainable and resilient future. The conference is organised by the EU-funded eLTER PLUS Advanced Community project (Grant Agreement No. 871128) and supported financially by the University of Helsinki, the Federation of Finnish Learned Societies, Metsämiesten Säätiö Foundation, and the Atmosphere and Climate Competence Center Flagship of the Research Council of Finland.

The eLTER-SO-Costs web application is a specialized tool designed to assist the eLTER (integrated European Long-Term Ecosystem, critical zone and socio-ecological Research) community in estimating the costs associated with upgrading and operating standard observations (SOs) across various eLTER sites. It provides a flexible and efficient approach to cost estimation by tailoring calculations to specific site characteristics, ensuring that cost assessments are relevant and accurate. The tool considers key factors such as the site category, habitat types, focus spheres, and the potential for co-location with other research infrastructures, all of which influence the costs. The application is designed to be highly adaptable, allowing users to customize the output according to specific needs and exclude or adjust certain predefined cost elements based on the unique conditions of their sites or platforms. The core functionality of the application allows users to input unique site-specific data and receive an automated, detailed annual cost breakdown for SOs. The eLTER-SO-Costs facilitates financial planning, enabling eLTER site managers to optimize their eLTER site management, reducing the time and effort traditionally spent on manual cost calculations, democratizing access to essential financial data for the broader eLTER community. The tool’s user-friendly interface ensures that site managers and researchers, even those without expertise in cost analysis, can efficiently plan for the long-term sustainability of their sites while meeting the scientific and operational demands of ecological monitoring.

“A continuous forest data set of 579 forest and peatland plots around the Hyytiälä Forest Station in southern Finland (61° 50′ N, 24° 17′ E). The majority of the plots were established for educational purposes to demonstrate the functioning of forests and peatlands as an ecosystem, their structure, growth, development, and different management practices. Some plots have been used for forest and peatland research works. The dataset includes information such as species, volume, number of stems, basal area and site fertility class per plot. The dataset also includes templates for future data collection, which can later be incorporated into the dataset.”

Pikeperch (Sander Lucioperca) belongs to main predatory fish species in freshwater bodies throughout Europe playing the key role by reducing planktivorous fish abundance. Two size classes of the young-of-the-year (YOY) pikeperch are known in Europe and North America. Our long-term fish survey elucidates late-summer size distribution of YOY pikeperch in the Lipno Reservoir (Czechia) and recognizes two distinct subcohorts: smaller pelagic planktivores heavily outnumber larger demersal piscivores. To explore molecular mechanisms accompanying the switch from planktivory to piscivory, we compared brain transcriptomes of both subcohorts and identified 148 differentially transcribed genes. The pathway enrichment analyses identified the piscivorous phase to be associated with genes involved in collagen and extracellular matrix generation with numerous Gene Ontology (GO), while the planktivorous phase was associated with genes for non-muscle-myosins (NMM) with less GO terms. Transcripts further upregulated in planktivores from the periphery of the NMM network were Pmchl, Pomcl, and Pyyb, all involved also in appetite control and producing (an)orexigenic neuropeptides. Noncoding RNAs were upregulated in transcriptomes of planktivores including three transcripts of snoRNA U85. Thirty genes mostly functionally unrelated to those differentially transcribed were alternatively spliced between the subcohorts. Our results indicate planktivores as potentially driven by voracity to initiate the switch to piscivory, while piscivores undergo a dynamic brain development. We propose a spatiotemporal spreading of juvenile development over a longer period and larger spatial scales through developmental plasticity as an adaptation to exploiting all types of resources and decreasing the intraspecific competition.

We live in a world characterized by rapid social, economic, and ecological changes, facing important environmental challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and pressures on natural resources. Addressing these issues requires world-class ecosystem research, driven by a well-connected, extensive community of experts, supported by advanced sites and facilities, and supported by openly shared and easily accessible data alongside capacity building programs. This is the mission of the eLTER Research Infrastructure (eLTER RI). Currently, in its preparatory phase, eLTER is on the path to becoming a fully-fledged Research Infrastructure. Central to this endeavor is the eLTER Cyber infrastructure (CI), which serves as the technical backbone for all data management and information services within eLTER RI. The Cyberinfrastructures aim is to support workflows and processes with modern software and cloud solutions to accommodate the requirements of the eLTER RI. CI is involved in the entire data life cycle, from ingestion to preservation and is composed by different components targeting different users, including data providers, data managers, and data users, as well as other service providers and research infrastructures. The primary requirement is the implementation of state-of-the-art data management, adhering to the FAIR principles. eLTER CI envisions various data management solutions and implementations, designed to be interconnected, forming a valuable collection of well-integrated tools and services. To this end, eLTER CI integrates EUDAT services, such as B2Share, to facilitate data integration workflows. Other solutions, like the Sensor Management System combined with a time series data management system, leverage the B2Inst registry for scientific instruments. This work provides an overview of the current system architecture and planning, offering a comprehensive insight into how digital services within the European landscape can be integrated into complex research infrastructures.

The paper presents an extensive dataset of the shallow reef fish communities and habitat characteristics in the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago (Southwest Atlantic). The data were collected from August to October 2006 in the Fernando de Noronha main island. To evaluate the shallow reef fish communities, 165 visual censuses were performed in eight different localities in the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago.

European biodiversity research infrastructures (BioRIs) play a critical role in addressing the escalating biodiversity crisis by providing data, tools, and services necessary for scientific research and policy-making. However, despite their potential, these infrastructures are often fragmented in terms of communication and coordination, scientific fields most impacted as well as the interoperability and cohesion of their services. This fragmentation impedes their ability to collaborate effectively and facilitate comprehensive solutions to biodiversity challenges. Motivated by the need to enhance the coherence and impact of European BioRIs, this study investigates four major infrastructures: Distributed System of Scientific Collections (DiSSCo), Integrated European Long-Term Ecosystem Research (eLTER), Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), and LifeWatch ERIC. Through surveys of managerial staff and literature tracking, we assess the communication and collaboration efforts within and across these infrastructures, evaluate their scientific impact, and explore the cohesion of their services and data. Our results show that while internal communication is stronger within individual BioRIs, cross-infrastructure collaboration is limited. Notably, eLTER and LifeWatch exhibit higher levels of internal interaction compared to DiSSCo and GBIF. Our study also highlights significant challenges in public engagement and data standardization. We conclude with recommendations for improving interoperability and communication to strengthen the role of BioRIs in addressing biodiversity issues at both European and global scales.

Gillnets are widely used in research and commercial fishery activities. As passive gear, gillnets can be selective and dependent on the diel migration of fish. In areas with limited littoral extent, inshore–offshore migration may cause bias in the gillnet catch. Our hypothesis was that some factors, such as gillnet saturation, fish depletion, or chemical cues, could be the cause of the bias. We used a total of 66 CEN gillnets deployed at Římov Reservoir parallel to the shore at different positions of littoral-pelagic gradient. Individual fish direction was recorded from inshore, offshore, or unknown direction (i.e., entangled fish). A total of 5791 fishes from nine different species were caught. For most fish, it was possible to determine their directivity, and most fish were captured in littoral or first pelagic gillnets. Shallower and deeper benthic gillnets differed in their bleak (Alburnus alburnus) catch. No significant differences were found between fish directions. At the species level, only asp (Leuciscus aspius) and ruffe (Gymnocephalus cernua) showed differences between the captured directions in one case. The results support the assumption that gillnet capture is a random process that to a great extent is connected to random local movements. This is good news for fish monitoring projects. Sampling catch is likely to reflect true changes in the fish community, and not the effects of the deployment of the sampling gear. The experiment also showed that fish directivity statistics can be used for investigation of fish behavior and gear performance.

Digital Twins are a new concept in the field of biodiversity (de Koning et al. 2023), one aspect is the user interface for interacting with digital twins. In the BioDT (Biodiversity Digital Twin) (BioDT 2022) project we are creating a graphical web interface (Martinovič et al. 2024) using the R Shiny framework, which allows small-scale data analysis to be done directly on the server running the web interface, while making it possible to offload a large-scale analysis to a supercomputer such as LUMI (Large Unified Modern Infrastructure). Additionally, we foresee that multiple prototype Digital Twins (pDTs) will be available as part of one web application. This brings multiple challenges in optimization of data flows for the computation and interaction with users, especially since data used by the pDTs, developed in the BioDT, are usually stored across multiple data sources. In the BioDT web application, we want to enable users to access different pDTs concerned with questions such as ecosystem services, biodiversity dynamics, DNA-related biodiversity tasks, pollinators, invasive species, disease outbreaks, and more. While some of these pDTs compute results at a remote server and provide only the newest results to the application, others aim to allow users to execute their own pDT runs with their own data and settings. This leads to many different user scenarios and impacts authentication and authorization flows, as well as data flows. In addition to this, we want to make the whole system comply with the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles as much as possible. For this, we need to support traceability of data, models, and pDT executions. This means that we advocate for data to be hosted at data providers with APIs for machine-to-machine interaction and extensive metadata support; models to be as open as possible and versioned; and to have a workflow execution orchestrator that can keep track of the models’ execution and their related inputs and outputs. In terms of data, we are using research infrastructures (RIs) such as GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) and eLTER (Integrated European Long-Term Ecosystem, critical zone and socio-ecological Research) for the input data streams and when it is not possible to use established RIs, we are using self-hosted services. This work is still in progress and some of the self-hosted datasets are still being used, but in the future, we are looking into the possibility of having a dynamic system that will support data formats that cannot be currently stored at the established RIs. Our colleagues at BioDT consortium are preparing a special data server (El-Gabbas et al. 2023) that can handle complex data processing and serve data through an API without the need to download data for multiple commonly used formats. Some of the BioDT pDTs leverage the computational strength of High-Performance Computing (HPC) clusters and in such cases, classical cloud workflow orchestrators are not an option due to the specific security policies of such centers. To solve this, we turned to the LEXIS Platform, which can execute predefined workflows on a combination of cloud and HPC resources, and track the executions and related execution metadata. We are looking into exporting the descriptions of the workflow executions to Research Object Crates (RO-Crates) and then uploading this information to a remote server, where users could check their execution settings later. A current main development focus is the question of how to tackle the challenge of multiple authentication systems. This is specifically of concern in the case of sensitive data, which need to remain secure and available only to selected people. Due to interactions with several systems, we are encountering authentication issues of multiple different identities that should be recognized as one. The simplest solution here is to use one platform for data storage, workflow execution and web application. However, in the future we hope to find a more general solution that would not require data transfer to a single platform, since this could lower the usage of the BioDT platform due to legal restriction on some data. Another challenge in optimization of the dataflows is to avoid downloading the same data repeatedly and to be able to provide users with relevant data in the web application as fast as possible, since long waiting time would result in people not using the web application. For these issues, we are considering a smart-caching mechanism, however such functionality is not yet defined.

The paper presents an extensive dataset of the shallow-reef fish communities and habitat characteristics in the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago (SW Atlantic). The data was collected from August to October of 2006 in the Fernando de Noronha main island, which belongs to the Brazilian Oceanic Islands - PELD/ILOC (https://deims.org/030bec0b-f6ac-4840-b226-af813258b14b). To evaluate the shallow-reef fish communities, 165 visual censuses were performed in eight different localities in the Fernando de Noronha Island. The dataset reports a comprehensive compilation of the shallow reef fish abundance, of eight localities of the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago. The dataset reveals spatial heterogeneity among the selected localities in terms of fish abundance, composition and size.

Bird populations respond rapidly to environmental change making them excellent ecological indicators. Climate shifts advance migration, causing mismatches in breeding and resources. Understanding these changes is crucial to monitor the state of the environment. Citizen science offers vast potential to collect biodiversity data. We outline a project that combines citizen science with AI-based bird sound classification. The mobile app records bird vocalisations that are classified by AI and stored for re-analysis. Additionally, it shows a shared observation board that visualises collective classifications. By merging long-term monitoring and modern citizen science, this project harnesses the strength of both approaches for comprehensive bird population monitoring.

Invasive alien species (IAS) threaten biodiversity and human well-being. These threats may increase in the future, necessitating accurate projections of potential locations and the extent of invasions. The main aim of the IAS prototype Digital Twin (IAS pDT) is to dynamically project the level of plant invasion at habitat level across Europe under current and future climates using joint species distribution models. The pDT detects updates in data sources and versions of the datasets and model outputs, implementing the FAIR principles. The pDT’s outputs will be available via an interactive dashboard. All input and output data will be freely accessible.

Pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) is a European fresh and brackish water piscivorous fish, important as a key predator and a valuable fisheries species. Despite concerns that some stocks are depleting due to overfishing and environmental changes, stock assessments are implemented sporadically. We provide an overview of data collection and population assessments currently used for nine pikeperch stocks across six European countries and apply a unified assessment framework (Bayesian surplus production models) to evaluate population status and trends. Our results show that three stocks, including two in the Baltic Sea, are strongly depleted, with estimated biomasses considerably lower than the biomass at maximum sustainable yield (BMSY). Other stocks are close to their estimated BMSY. Further, recent population trends suggest that only one stock (Kvädöfjärden) is increasing, whereas three (Curonian Lagoon, Lipno, Galtfjärden) are rapidly declining. In most cases the stocks with a favourable status or signs of recovery were also those for which strong management strategies have been implemented. Importantly, although most stocks are strongly targeted by recreational fishing, estimates of recreational catch are highly uncertain. We highlight an urgent need to improve pikeperch scientific monitoring and assessment of recreational catches.

The information provided here represents the EBV workflow templates collected during the EuropaBON online workshop on Essential Biodiversity Variable (EBV) workflows from 22–24 February 2023. The templates were designed to capture comprehensive descriptions about the three workflow components (data collection and sampling, data integration, and modelling) that are typical for generating EBVs. Recognising the potential value of those EBV templates for European biodiversity monitoring, our objective is to share them for enhancing transparency, knowledge exchange and collaboration, and promoting the operationalisation of EBVs across Europe. EuropaBON (https://europabon.org/) is a Horizon 2020 research and innovation action funded by the European Commission that seeks to co-design a European Biodiversity Observation Network. This network aims to bridge the gap between the biodiversity data needs of policy-makers and authorities on the one hand and the existing reporting streams and available data sources on the other hand, considering both present obligations and forthcoming policy needs. Essential Biodiversity Variables (EBVs) are a central concept of EuropaBON as they provide a standardised framework for biodiversity monitoring and reporting. In 2023, EuropaBON had identified 70 EBVs (Junker et al., 2023) that are policy-relevant for the EU, and measurable with available and existing technologies and with a proven track record of feasibility in ongoing initiatives. EBVs require workflows to process the raw data (primary observations) through data integration and modelling into spatially-explicit EBV data products (Kissling et al., 2018; Schmeller et al., 2017). These workflows can be broken down into three main components (data collection and sampling, data integration, and modelling), with additional aspects of data interoperability and IT infrastructure being recognised as crucial for transnational data streams (Kissling & Lumbierres, 2023). To capture information about the EBV workflows, an online workshop was held on 22–24 February 2023 with 520 registered participants from 49 countries, covering a large range of expertise (Lumbierres & Kissling, 2023). Participants contributed information on EBV workflow components and advanced monitoring techniques, discussed initiatives, and identified tools and requirements for implementing 70 proposed EBVs. The information from the workshop participants was collected through pre-defined EBV workflow templates (provided as Google Docs). Templates were organised into rows representing the workflow components (‘Data collection and sampling’, ‘Data integration’, and ‘Modelling’) and columns reflecting the levels of maturity (‘Current initiatives’, ‘Emerging tools and projects’ or ‘Future needs’). Prior to the workshop, some information on existing workflows was pre-filled based on previous EuropaBON deliverables, namely an assessment of the current biodiversity monitoring gaps in the EU (Santana et al., 2023) and an assessment of current EU monitoring workflows and bottlenecks (Morán-Ordóñez et al., 2023). After the workshop, the EBV workflow templates were processed to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information. Each listed initiative was verified to be part of an active biodiversity monitoring scheme and pertinent to the specific EBV under consideration, cross-referencing with the initiative’s websites and other data collected by the EuropaBON deliverables (Morán-Ordóñez et al., 2023; Santana et al., 2023). Moreover, we ensured correct alignment of each initiative and listed requirements and needs with the appropriate workflow components and maturity levels. The EBV workflow templates provide insights into the current biodiversity monitoring landscape in Europe and how EBV production could be operationalized at the EU level. They offer detailed information about ongoing initiatives and projects, methodologies, and technologies that can be used to generate EBVs at a continental scale. Nevertheless, it is important to note that they do not encompass an exhaustive list of all ongoing or proposed initiatives of biodiversity monitoring in all member states of the EU. It is suggested to use them as a starting point and baseline for the further development of EBVs in a European context.

Understanding inter-annual variation in the density of young-of-the-year fish is an important tool for assessing stock status and guiding management decisions. We analyzed data spanning from 2003 to 2022 collected at Lipno Reservoir in Czechia. The study aimed to identify factors influencing the density of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca), a valuable predatory fish species in European waters. A bimodality test for the size class distribution has revealed the existence of two distinct YOY cohorts: extremely small (ES) and ordinary fingerlings. Using the Bayesian horseshoe prior method with 37 potential predictors, followed by linear regression, we observed that certain environmental factors similarly influenced both cohorts. Higher temperatures during spring and summer, coupled with increased densities of large and medium-sized cladocerans, positively affected the density of both cohorts. However, distinct influences were observed: for ordinary fingerlings, increased summer precipitation and a lower abundance of predators were beneficial, whereas, for ES fingerlings, summer copepod density emerged as an additional positive factor. This study emphasizes the importance of a detailed investigation of factors influencing pikeperch recruitment. Examining these drivers provides a clearer insight into the causes of variations in the early life stage, which is crucial for monitoring and managing populations in temperate reservoirs.

This repository hosts the information used to build the eLTER SO Costs web application. This tool is a specialized resource designed to assist the eLTER (European Long-Term Ecosystem Research) community in estimating the costs associated with upgrading and operating standard observations across various eLTER sites. The essence of this tool lies in its ability to adapt calculations based on unique site-specific criteria, ensuring tailored cost estimations. Key factors taken into consideration include the site category, the habitats, the focus spheres, and the potential co-location with other Research Infrastructures, which cover the costs of specific standard observations. The goal of this tool is to provide a user-friendly, efficient, and reliable means for the eLTER community to plan and allocate resources effectively.

Bird populations respond rapidly to environmental change making them excellent ecological indicators. Climate shifts advance migration, causing mismatches in breeding and resources. Understanding these changes is crucial to monitor the state of environment. Citizen science offers vast potential to collect biodiversity data. We outline a project that combines citizen science with AI-based bird sound classification. The mobile app records bird vocalizations that are classified by AI and stored for re-analysis. Also, it shows a shared observation board that visualizes collective classifications. By merging long-term monitoring and modern citizen science, this project harnesses both approaches’ strengths for comprehensive bird population monitoring.

The paper presents an extensive fish sampling dataset spanning a long-term period from 2010 to 2019. The data were collected in Lenta Marina, an upstream area in the Minho Estuary of the NW Iberian Peninsula, which belongs to a LTSER (Long-Term Socio-Ecological Research) platform. To capture fish, fyke nets were utilised as the sampling method and deployed at Lenta Marina. This dataset offers valuable insights into the abundance of each collected taxa recorded over time.

This document contains the lecture slides for “Best Practices in Research Data Management”, which was a lecture given as part of the course FOR-284: Methods in Plant Ecophysiology at the University of Helsinki, Finland, in February 2024. The lecture is designed as a first introduction to best practices in research data management, aiming to educate students on the importance of adhering to good data management practices. It includes examples and references to further resources on the topic.
Despite great promise for understanding the impacts and extent of climate change and extreme weather events on aquatic animals, their species, and ecological communities, it is surprising that electronic tagging and tracking tools, like biotelemetry and biologging, have not been extensively used to understand climate change or develop and evaluate potential interventions that may help adapt to its impacts. In this review, we provide an overview of methodologies and study designs that leverage available electronic tracking tools to investigate aspects of climate change and extreme weather events in aquatic ecosystems. Key interventions to protect aquatic life from the impacts of climate change, including habitat restoration, protected areas, conservation translocations, mitigations against interactive effects of climate change, and simulation of future scenarios, can all be greatly facilitated by using electronic tagging and tracking. We anticipate that adopting animal tracking to identify phenotypes, species, or ecosystems that are vulnerable or resilient to climate change will help in applying management interventions such as fisheries management, habitat restoration, invasive species control, or enhancement measures that prevent extinction and strengthen the resilience of communities against the most damaging effects of climate change. Given the scalability and increasing accessibility of animal tracking tools for researchers, tracking individual organisms will hopefully also facilitate research into effective solutions and interventions against the most extreme and acute impacts on species, populations, and ecosystems.

Research Infrastructures (RI) are facilities that offer resources and services for research communities to conduct research and promote innovation. RI can be a single site or distributed and include major scientific equipment, collections, archives or scientific data, computing systems and communication networks. Interoperability is an important aspect of Open Science (OS). It refers to the ability of different systems and organizations to work together and exchange information seamlessly. Interoperability involves establishing common standards, formats, and protocols that enable different systems or components to communicate with each other and exchange the data without loss or distortion of information. Data interoperability addresses challenges related to data compatibility, structure, semantics, and technical integration. It involves defining and adhering to shared data models, schema, and metadata standards, as well as utilizing common communication protocols and interfaces. In the context of OS, interoperability allows for the integration and interconnection of research infrastructures, reducing the fragmentation of the research and innovation ecosystem and avoiding the duplication of effort. Achieving interoperability across resources and services within RIs can present several challenges. Most of the interoperability challenges can be divided into two blocks, namely technical and social challenges. In conclusion, RIs are crucial for promoting scientific research and driving innovation in various fields. To maximize their impact, achieving interoperability is a key challenge that needs to be addressed. Centralized hubs of standards, such as common vocabularies and data formats, can facilitate communication and collaboration among research infrastructures. Improved communication and coordination among research infrastructures can also help prevent the duplication of effort and increase efficiency. These initiatives are essential for accelerating scientific progress, bridging gaps, and improving the usability of RIs.

Centered on biodiversity data, this presentation provides a concise yet comprehensive introduction to the critical significance of publishing data papers. Delving into the specifics, the session sheds light on key aspects of Biodiversity Data Journal. Moreover, the presentation shows a first-hand exploration of the publication process within Biodiversity Data Journal, as the presentation incorporates personal impressions and experiences. This insider’s perspective offers a nuanced understanding of the intricacies involved in bringing data papers to fruition within the journal.
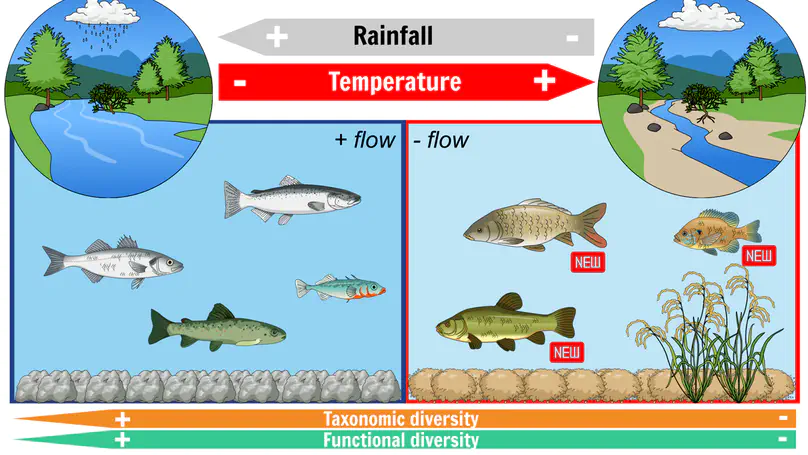
As the effects of climate change continue to intensify, non-native species are becoming more prevalent in estuarine ecosystems. This has implications for the taxonomic and functional diversity of fish communities. Historically, biodiversity has been a synonym of taxonomic diversity, however this approach often fails to provide accurate insights on ecosystem functioning and resilience. To better understand how climate change is impacting fishes and their traits’ composition, a long-term dataset from Minho Estuary (NW Iberian Peninsula) fish assemblage was analyzed. The results suggest that climate change and extreme weather events altered the prevailing trait modalities of fishes, which led to the overall decrease in functional diversity of the fish assemblage over the course of a decade. This decrease is associated to the loss of some trait modalities that are exclusively found in native species. On the other hand, the invasive species added novel traits associated with the conditions of high temperatures and low precipitation regime currently observed in the studied area. Our results highlight that the shift in the presence and dominance of some traits is directly influenced by climatic changes. Also, despite the addition of novel modalities by the invasive species, the fish assemblage is now less functional and taxonomically diverse than previously.

This dataset contains the information on the micro elemental composition of Sagitta otoliths of Pike-Perch (Sander lucioperca) collected in Lipno Reservoir (Czechia). The dataset covers a wide range of micro elemental components (barium, calcium, copper, potassium, lithium, magnesium, manganese, sodium, rubidium, strontium and zinc) obtained from the otolith cores and rims of these fish specimens. The dataset includes readings from Pike-Perch directly collected in Lipno Reservoir, as well as from those reared in facilities and later introduced into the reservoir.

The paper presents an extensive fish sampling dataset spanning a long-term period (weekly) from 2010 to 2019. The data was collected in Lenta Marina, an upstream area in the Minho Estuary of the NW Iberian Peninsula. To capture fish, fyke nets were utilized as the sampling method. This dataset offers valuable insights into the abundance of each collected taxa, recorded per date.
The dataset reports a comprehensive compilation of fish abundance data, providing a detailed record of how the fish community has changed over time. The dataset clearly shows a trend where the amount of fish from invasive taxa exceeds the count of fish from native taxa.
Global climate change has been altering freshwater ecosystems by impacting many ecological processes, including individual fish growth. Predictions of responses of local fish populations to future environmental change can draw inferences from past long-term biochronological data. In this study, we reconstructed individual growth pattern of one of the most valuable predatory species in European inland waters, pikeperch (Stizostedion lucioperca), using back-calculated length from their otoliths. Samples were collected at the Lipno reservoir (Czech Republic) between 2008 and 2020. We used linear mixed-effects models to investigate how individual state and environmental conditions affect the somatic growth of the local pikeperch population. We found that individual growth rates increased with temperature and tended to be higher when chlorophyll-a concentration was higher, and water transparency was lower. This suggests the species will likely benefit from the warmer waters predicted in future climate scenarios. However, the decreasing nutrient loading associated with efforts to curb eutrophication in Central Europe may offset these benefits. Together, these results provide a better understanding of how multiple environmental factors, directly and indirectly, influence the somatic growth of pikeperch in long term.

As the effects of climate change continue to intensify, non-native species are becoming more prevalent in estuarine ecosystems. This has implications for the taxonomic and functional diversity of fish communities. Historically, biodiversity has been a synonym of taxonomic diversity, however this approach often fails to provide accurate insights on ecosystem functioning and resilience. To better understand how climate change is impacting fishes and their traits composition, a long-term dataset from Minho Estuary (NW Iberian Peninsula) fish assemblage was analyzed. The results suggest that climate change and extreme weather events are altering the prevailing trait modalities of fishes, which led to the overall decrease in functional diversity of the fish assemblage over the course of a decade. This decrease is associated to the loss of some trait modalities that are exclusively found in native species. On the other hand, the invasive species added novel traits associated to the conditions of high temperatures and low precipitation regime currently observed in the studied area. Our results highlight that the shift in the presence and dominance of some functional traits is directly influenced by climatic changes. Also, despite the addition of novel modalities by the invasive species, the fish assemblage is now less functional and taxonomic diverse than previously.

The dataset contains data from fyke nets deployed in the Minho Estuary (Portugal) from 2010 to 2019. The fyke nets were used for fish sampling and data collection. The sampling frequency varied but, on average, data was collected weekly using five different fyke nets. However, due to technical issues (e.g. lost or damaged fyke nets), the sampling pattern is not constant, with some fyke nets staying underwater for shorter or longer periods, and occasionally having fewer than five fyke nets per parentEventID. The dataset includes various terms such as parentEventID, eventID, eventDate, year, startDayOfYear, endDayOfYear, country, countryCode, geodeticDatum, decimalLatitude, decimalLongitude, coordinateUncertaintyInMeters, DEIMS.iD, habitat, basisOfRecord, samplingProtocol, sampleSizeValue, sampleSizeUnit, samplingEffort, occurrenceStatus, occurrenceID, organismQuantity, organismQuantityType, degreeOfEstablishment, vernacularName, scientificName, acceptedNameUsageID, taxonRank, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and scientificNameAuthorship.

Fish are an important component of aquatic ecosystems, thus representative and reliable assessments of their population variables are essential for a variety of ecological applications, management and conservation. Determining Fish Density per actual Spatial Unit (volume or area, FDSU) as a measure of absolute fish quantity is of particular interest. Gillnets are undoubtedly one of the most common and important methods for assessing fish populations in large lentic waters. However, direct calculating of FDSU from gillnet catches is impossible because of the passive nature of this method, and to date there is no reliable model for calculating FDSU from gillnet catches. This weakness largely limits the use of gillnet data for applications requiring FDSU estimates.
The aim of this study was to calibrate gillnet catches using FDSU obtained by active methods (beach seine nets and hydroacoustics) to develop a tool for assessing FDSU from gillnet catches. To achieve this goal, we compared gillnet biomass to fish biomass estimated from the active methods, both of which cover similar spatiotemporal niches. This comparison was performed using a statistical approach based on the recognition of non-negligible random measurement error in both the explanatory (active methods) and response (gillnets) variables.
We found a strong positive linear relationship between fish biomasses sampled with gillnets and with active methods. The slope of the fitted linear model was similar when comparing gillnets with the two active methods. The statistical method used allowed for the inclusion of error in the biomass estimates with gillnets and active methods, refining the credible intervals of the estimated relationship. The effect of gillnet effort on model accuracy was simulated to show how increased effort narrows the credible interval. Finally, comparison with previously published relationships revealed a large but explainable discrepancy between our model and previous models.
Our study showed that conversion of gillnet biomass to biomass per actual spatial unit is possible. The effective sampling area of one square meter of gillnet was determined to be 8 m2 of waterbody surface area when European standard 12 mesh-sizes gillnets are used, and 5 m2 when four larger meshes are added to the European standard gillnets. Our model further stressed the impact of increased sampling effort on reducing estimation variability and shows that the model may be dependent on the fish community.

Habitat complexity of freshwater ecosystems has been decreasing due to human impacts. Therefore, conservation and environmental management actions have intensified in the recent years. Artificial floating islands (AFIs) are one environmental management action intended to promote the populations of aquatic organisms. In this study, we installed eight AFIs in the littoral area of Lipno Reservoir, Czech Republic and covered them with local wetland vegetation to study the impact of this mitigation action on the fish community. The AFIs were sampled by Point Abundance Sampling Electrofishing (PASE). The AFIs were mainly inhabited by juvenile roach (Rutilus rutilus) and perch (Perca fluviatilis), with densities one to two orders of magnitude higher than in the surrounding control sites. Juvenile catfish (Silurus glanis) and adult northern pike (Esox lucius) were apex predators that were recorded exclusively at AFIs. More fish were captured in AFIs than in control areas (up to 29.2 times more). Even AFIs of simple construction harboured significantly more age 0 + and juvenile fish than control areas, confirming their potential to serve as nursery ground for age 0 + fish in lentic systems. Artificial floating islands can be used to support juvenile fish in the conditions of impoverished littoral structured habitat.
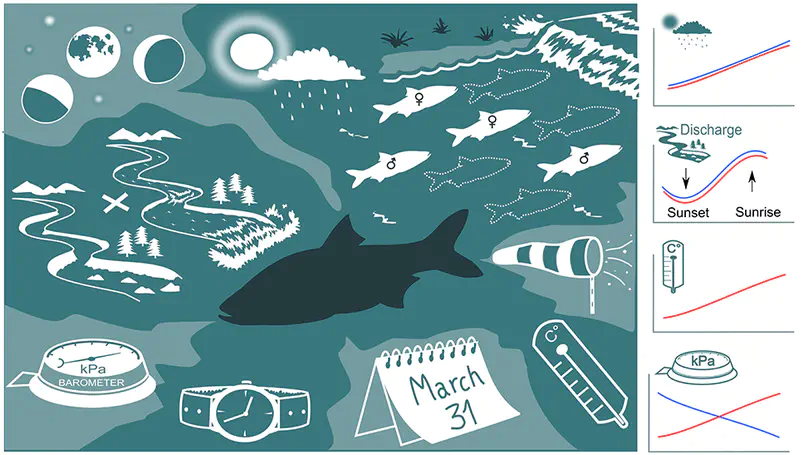

Background Animal migrations are periodic and relatively predictable events, and their precise timing is essential to the reproductive success. Despite large scientific effort in monitoring animal reproductive phenology, identification of complex environmental cues that determine the timing of reproductive migrations and temporal changes in the size of reproductive aggregations in relation to environmental variables is relatively rare in the current scientific literature. Methods We tagged and tracked 1702 individuals of asp ( Leuciscus aspius), a large minnow species, and monitored with a resolution of one hour the size of their reproductive aggregations (counts of sexes present at the breeding grounds standardized by the sum of individuals in the season) over seven breeding seasons using passive integrated transponder tag systems. We examined the size of reproductive aggregations in relation to environmental cues of day number within a reproductive season (intra-year seasonality), water temperature, discharge, hour in a day (intraday pattern), temperature difference between water and air, precipitation, atmospheric pressure, wind speed and lunar phase. A generalized additive model integrating evidence from seven breeding seasons and providing typical dynamics of reproductive aggregations was constructed. Results We demonstrated that all environmental cues considered contributed to the changes in the size of reproductive aggregations during breeding season, and that some effects varied during breeding season. Our model explained approximately 50% of the variability in the data and the effects were sex-dependent (models of the same structure were fitted to each sex separately, so that we effectively stratified on sex). The size of reproductive aggregations increased unimodally in response to day in season, correlated positively with water temperature and wind speed, was highest before and after the full moon, and highest at night (interacting with day in a season). Males responded negatively and females positively to increase in atmospheric pressure. Conclusion The data demonstrate complex utilization of available environmental cues to time reproductive aggregations in freshwater fish and their interactions during the reproductive season. The study highlights the need to acquire diverse data sets consisting of many environmental cues to achieve high accuracy of interpretation of reproductive timing.

Freshwater protected areas are designated parts of the inland waters that restrict human activities. They were created as a mechanism to combat the decline of fauna and flora of the world. Some authors have questioned their actual effectiveness in terms of the purpose of protecting endangered fauna and flora. We conducted an experiment in Lipno reservoir in the Czech Republic to evaluate the impact of protection against angling pressure on the fish community. We selected data from two years of gill netting and analyzed the difference between areas of low anthropogenic impact (LAI) and those of high anthropogenic impact (HAI) in terms of abundance, biomass, standard length, and diversity indices. Three groups of fish were found to prefer protected areas with low anthropogenic pressure: 1. YOY (Young-of-the-year) perch (Perca fluviatilis), the dominant of the young-of-the-year fish community. 2. Pike (Esox lucius), wels catfish (Silurus glanis) and rudd (Scardinius erythrophthalmus), which were not found in HAI areas at all. 3. Larger individuals of pikeperch (Stizostedion lucioperca), which survived better in LAI areas. Some factors may affect LAI, such as illegal poaching or setting out food bait to attract the fish outside. Another factor that can be considered is the migration of fish, either to forage or to reproduce, since the LAI areas are open to the reservoir. The areas of LAI act as protective habitats for heavily exploited predatory fish species and increase fish diversity indexes. The example of the protected and low-impact areas of Lipno should be followed in other water bodies with high fishing pressure and anthropogenic impact.

Anthropogenic activities continue to pose the greatest challenges to freshwater ecosystems. Therefore, long-term monitoring is essential for the management and conservation of these resources. Monitoring programs for freshwater bodies often use a range of indicators, including biological elements such as fish. Existing European standard provides a depth-stratified gillnet sampling approach mainly in benthic habitats and at the deepest part of lakes to account for the uneven distribution of fish. However, the commonly used CEN (European Committee for Standardization) protocol does not weight sufficiently habitat volumes and underrepresent pelagic habitats to calculate whole-lake catch and biomass per unit effort (CPUE and BPUE, respectively). Extended European standard gillnet (4 larger mesh-sizes added in the geometric series) catch data collected over 18 years (2004–2021) in Římov Reservoir (Czech Republic) were used for a method comparison on indices for relative abundance and biomass of fish: CEN protocol without volume-weighting and two volume-weighted approaches. We also evaluated changes in species composition and trends in these fish population over time. Results indicated interannual changes in species composition, relative abundance, and biomass of fish community. The CEN protocol tended to put greater emphasis on benthic habitats which generally have larger CPUE and BPUE. Consequently, the two volume-weighting approaches produced lower estimates of the two parameters, with the exception of the most dominant pelagic bleak Alburnus alburnus (L.). All approaches consistently showed an increasing trend in whole-reservoir fish abundance and a decreasing trend in biomass over the study period. Following our assessment, we put forward the volume-weighting approach that considers the Volume of the depth Stratum (VOST) for weighting as the most realistic approximation of fish populations and therefore recommend its use.

Invasive alien species pose a serious threat to biodiversity. They frequently compete with native species for resources, resulting in the decline or extinction of the latter. Native crucian carp (Carassius carassius) faces a severe decline in European waters and has become critically endangered in many European countries. Possible ecological mechanisms of the rapid decline of the crucian carp attributable to resource competition with the invasive Carassius gibelio were identified. A field study was combined with a controlled experiment to compare (i) standard length–weight relationships and growth patterns in 12 Czech and Swedish ponds in which the species occur alone or in syntopy, and (ii) individual growth and food utilization under the same conditions. The growth increment of C. gibelio was greater than that of C. carassius under the same experimental conditions (mean increase in weight: C. gibelio, 21.7%; C. carassius, 5.2%; increase in standard length: C. gibelio, 6.3%; C. carassius, 2.0%), suggesting that C. gibelio uses food resources more efficiently than C. carassius does. Moreover, larger C. carassius individuals did not grow, whereas growth of C. gibelio individuals was largely independent of standard length. Field data suggested that C. gibelio grew faster and were heavier than C. carassius of the same standard length in four Czech ponds where they occurred together. Individual weight-at-length declined in C. carassius in the presence of C. gibelio, especially in more dense populations, whereas the weight-at-length of C. gibelio remained similar. Taken together, these results imply that C. gibelio has better competitive abilities for food than C. carassius and provide novel support for the long-standing hypothesis that the introduction and spread of C. gibelio causes the decline of C. carassius in European waters.
The impact of barnacle epibionts on the condition of the shore crab Carcinus maenas was studied for the western Wadden Sea population. Approximately 39% of the crabs were fouled with the barnacle Balanus crenatus. Although the morphological Fulton’s K condition decreased by 5.8% in fouled crabs, Linear Mixed-Effects Models (LMM) showed that only the energetic condition of the crabs was significantly affected by fouling. The energy density of fouled crabs was consistently poorer (4.1% in AFDW; 8.7% in dry weight) than that of non-fouled crabs, especially in females and green forms in dry weight (12.8% and 11.4% reduction, respectively). Cumulative infection with Sacculina carcini, detected in 4.5% of the fouled crabs, additionally reduced by 14.3% the energy density in dry weight and almost to half of the total energy of the fouled crabs. Impacts of energy density reduction on crabs’ growth and reproduction are discussed.

Ligula intestinalis (Linnaeus, 1758) is a tapeworm parasite with a worldwide distribution that uses a wide variety of fish species as its second intermediate host. In the present study, we investigated the prevalence and population genetic structure of plerocercoids of L. intestinalis in five common cyprinoid species, roach Rutilus rutilus (Linnaeus), freshwater bream Abramis brama (Linnaeus), white bream Blicca bjoerkna (Linnaeus), bleak Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus), and rudd Scardinius erythrophthalmus (Linnaeus), collected in six water bodies of the Czech Republic (Milada, Most, Medard, Jordán, Římov and Lipno). Of the six study sites, the highest frequency of parasitism was recorded in Lake Medard (15%). The overall prevalence rate among the species was as follows: roach > rudd ≥ freshwater bream > bleak > white bream. Two mitochondrial genes (cytb and COI) were used to compare the population genetic structure of parasite populations using selected samples from the five fish species. The results of the phylogenetic analysis indicated that all populations of L. intestinalis were placed in Clade A, previously identified as the most common in Europe. At a finer scale, haplotype network and PCoA analyses indicated the possible emergence of host specificity of several mtDNA haplotypes to the freshwater bream. Moreover, pairwise Fixation indices (FST) revealed a significant genetic structure between the parasite population in freshwater bream and other host species. Parasite populations in roach not only showed the highest rate of prevalence but also depicted a maximum number of shared haplotypes with populations from bleak and rudd. Our results suggest that recent ecological differentiation might have influenced tapeworm populations at a fine evolutionary scale. Thus, the differences in prevalence between fish host species in different lakes might be influenced not only by the parasite’s ecology, but also by its genetic diversity.

The removal of planktivorous fish results in ecosystem changes that increase water transparency and decrease the risk of harmful algal blooms. In many situations, complete eradication of fish is necessary to improve water quality, which can also protect natural populations. In this work, we construct a generic fish-zooplankton (FZ) model and we determine conditions to eradicate the fish population through repeated fish removal. The model accounts for the weight and age of fish, and is described by a system of ordinary differential equations with impulsive effects representing the reproduction process and fish removal. We demonstrate that the survival and extinction of fish can be determined from the roots of a polynomial, whose coefficients depend on maximal fecundity, mortality rates, and catching effort. If all roots of the polynomial lie within the unit circle, then eradication is ensured. To illustrate our results, we show the importance of removing young fish, and not only adults, to achieve eradication.

Despite the increasing awareness of climate change, few studies have used the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) scenarios to simulate the effects of climate change on estuarine populations of crustaceans. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of temperature and salinity fluctuations on the population dynamics of the shore crab Carcinus maenas at the southern edge of its native range. To this end, a population dynamics model was developed based on experimental and literature data on the biology, ecology and physiology of the species. Results showed that the shore crab will be more affected by changes in temperature than in salinity. The parameter sensitivity analysis revealed that the larval phase of the species is the most sensitive stage of the shore crab life cycle. Three IPCC scenarios (SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5, and SSP3-8.5) were used to simulate the effects of temperature increase on the population of C. maenas in the near- (2040), mid- (2060), and long-term (2100). Two scenarios of drought conditions accompanied by the estimated salinity change were also simulated (10 % and 40 % drought). Results suggested that slight increases in temperature (up to 2 °C) lead to a strong increase on the density of C. maenas in the mid-term, while further temperature increases lead to a decline or local extinction of the shore crab population at the southern edge of its distribution range. Salinity increase in the estuary had a negative effect on the shore crab population. Given the importance of the species to temperate coastal ecosystems, both population increase and local extinction are likely to have significant impacts on estuarine communities and food webs, with unknown ecological and socioeconomic consequences.

To understand the spatiotemporal overlap in the habitat use of sympatric predators, we studied longitudinal activity and reservoir section and depth use of pike (Esox lucius), pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) and catfish (Silurus glanis) in the Římov Reservoir, using an autonomous telemetry system for 11 months. We found significant differences among these species in studied parameters that varied considerably over tracked period. Pike consistently used the same sections of the reservoir, while pikeperch and catfish frequently visited a tributary during the warm season (late spring and early autumn), and moved closer to the dam during the cold season (late autumn to early spring). Pike longitudinal activity was highest in the cold season, pikeperch in the warm season, and catfish activity peaked in both seasons. Overlap in the depth use among species was higher in the warm season, when all species used the upper layer of the water column, and lower in the cold season, when pikeperch and catfish used deeper areas. These results demonstrated overlay and temporal variation of habitat use among these predators, as well as potential spatiotemporal space for their direct ecological interactions.
Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent as a result of climate change, and the increasing frequency of these events may lead to significant changes in fish assemblages. In this sense, this work aimed to study the effects of climate change and extreme weather events on fish assemblages in the Rio Minho estuary (Portugal). Between 2010 and 2019, continuous weekly sampling with fyke nets was carried out to assess the dynamics of fish assemblages in the estuary. In addition, temperature and precipitation data were obtained from satellite information to assess the relationship between climatic variables and fish composition, structure, and diversity. Fish populations changed significantly over time, becoming less diverse and largely dominated by a few, mostly invasive species (e.g., carp, goldfish, pumpkinseed, and tench), while the abundance of most native species declined over the years (e.g., panjorca, stickleback, and shad). High temperatures and low precipitation negatively affected native species, while the invasive species benefited from increased temperatures and extreme weather events (droughts and floods).
Climate is a major driver of species distribution and biological invasions worldwide. In this study, we combined the catches of a widespread and invasive species, the common carp (Cyprinus carpio), with climate data to assess the importance of climate variables on the ability of the species to maintain self-sustaining populations in European lakes. Data were collected on common carp populations in 378 lakes in six European countries over a 16-year period (551 sampling campaigns). All catches followed the same standardized sampling procedure (European CEN gillnets). Climate data consisted of daily averages of air temperature and precipitation. Population self-sustainability was determined by the relative catches of different size classes and the presence of juveniles. The climate data were used to train a classification tree model to characterize the effects of climate on common carp population viability. Results indicated that climate is an important predictor of common carp population viability, which is particularly enhanced under dry conditions and elevated temperatures during spring and summer months. Areas of high population viability strongly overlapped with the invasive range of the species. According to Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) climate projections, some areas where common carp currently have a low probability of maintaining viable populations will shift toward climatic conditions that enhance their viability and invasion potential.

Animal behaviour interacts with various relationships within biota, and its variation among individuals may cause bias in behavioural research because of its impact on sampling efficiency. In this study, we simultaneously recorded fish behaviour during the reproductive season by passive telemetry and sampled a fish population using an active sampling method by boat electrofishing. A total of 1479 individuals of the cyprinid fish asp (Leuciscus aspius) were tagged, and their reproductive behaviour was recorded using passive telemetry systems in 2015–2020. We investigated whether capture probability was related to fish behaviour during reproduction (length of spawning, number of individual visits to spawning grounds, proportion of time spawning, arrival date and average daily arrival time). Overall, males were more likely to be captured than females (30 ± 4% standard error (SE) vs. 20 ± 3% SE probability) when present in the area. Traits favouring the odds of being captured differed between sexes and included the length of presence, proportion of time invested in spawning and average daily arrival time in males; in females, the capture probability was related to the length of presence and arrival date. This study suggests that even a large sample obtained using active gear may not represent the entire population’s behaviour because of behavioural-related bias in a population.

Gillnetting is a technique commonly used in relative abundance and biomass estimates of fish. However, due to its passive nature, the direct recalculation of the catch to reservoir volume or area is not trivial. This issue is often solved by using hydroacoustics, which provides information about fish density, though without the ability to distinguish species. However, the precision of such density estimates are also questionable. In this study, we estimated the abundance and biomass of dominant fish species before and after a biomanipulation program (fish removal) in 2020 using gillnetting and hydroacoustic surveys in a temperate reservoir. Between the two sampling periods, nearly 27,000 individuals (9000 kg) older than 0 + of bleak (Alburnus alburnus) and bream (Abramis brama) were removed during the biomanipulation program. Decreases in abundance and biomass estimates were expected for both techniques and both species. The gillnet decrease was 68% in CPUE (catch per unit of effort) and 48% in BPUE (biomass per unit of effort) for both species and all gillnets grouped together. Hydroacoustic observations showed a decrease of approximately 79% in abundance and 74% in biomass after fish reduction. Considering the numbers and biomass of fish removed, the absolute hydroacoustic estimates were underestimated for fish abundance but credibly estimated for biomass. The average weight of the fish taken was between the values of the fish caught with gillnets and the weights determined by hydroacoustics. In terms of results, both methods appear to be a suitable tool for estimating fish abundance and biomass in large inland waters, although the spatial and temporal distribution of fish of different sizes should be considered when using different sampling methods for fish monitoring.
Internal seiches are common in stratified lakes, with significant effects on stratification patterns, hydrodynamics and vertical nutrient transport. In particular, seiches can change the vertical distribution of the thermocline and the cold hypolimnetic and warm epilimnetic water masses by several metres on a timescale of a few hours, leading to rapid and strong changes in temperature profiles and oxygen availability, with profound effects on mobile and sessile organisms. This could affect fish communities directly, through physiological stress and elevated mortality, and indirectly, through prey distribution. The aim of this study was to analyse the effects of internal seiche dynamics on lacustrine fish behaviour, and to characterise fish reaction patterns, with the main focus on vertical movement of fish in the vicinity of a shifting thermocline, and avoidance of cold hypolimnetic water. The analysis was based on acoustic telemetry data from Lake Milada, a post‐mining lake in the Czech Republic, with a total of 61 tracked individuals of four species: northern pike (Esox lucius), wels catfish (Silurus glanis), tench (Tinca tinca) and rudd (Scardinius erythropthalmus). The effects of seiche dynamics on the four species studied were weak but significant during the day, while at night they affected only rudd. Upward seiches elicited stronger responses in fish than downward seiches, and the impacts occurred only during the strongest seiche events. Thermocline shifting during seiche events may induce a transient reduction in habitat for seiche‐reacting species, and thus affect predation and other inter‐ and intra‐specific interactions, as well as fish community dynamics. Seiche had a significant effect on the four studied species during the day, but only on rudd during the night.

Knowledge on population dynamics of ecosystem’s key-species is invaluable to understand how populations will respond to natural and human-induced perturbations. The amphipod Echinogammarus marinus is a key-species from European estuarine habitats with a distribution ranging from Norway to Portugal [1]. The present article contains supportive data related to a research article entitled ‘Comparing production and life-history traits of a key amphipod species within and between estuaries under different levels of anthropogenic pressure’ [2]. The present dataset presents the density, biomass, fecundity, and production of E. marinus in three estuaries under different anthropogenic pressure and, within each estuary, at three sampling sites, which differed in terms of the distance to the estuary mouth, vegetation cover, and organic matter content. Monthly environmental abiotic data and seasonal concentration of PAH and other contaminants are also provided. Sampling took place monthly for 13 months at low tide on intertidal mudflats. At each site, Fucus fronds containing E. marinus individuals were randomly collected. All E. marinus individuals were counted, sexed, and measured under a binocular stereo microscope to estimate the density and the biomass of E. marinus in Fucus fronds. Finally, the annual production of E. marinus at each sampling site was estimated through the size-frequency method. This dataset may be used to compare population traits of E. marinus populations across different estuaries and it may overall assist designing studies regarding population dynamics and designing management strategies in coastal systems, namely targeting at habitat conservation and restoration.

Inter-population variability may arise as a response to adverse natural and anthropogenic stressors. The dynamics of a key amphipod species (Echinogammarus marinus) was followed during ≈ 1-year at its southerly range (NW Portugal), in three estuaries with different levels of anthropogenic pressure (High - Ave estuary; Moderate - Mondego estuary; Low - Minho estuary). We hypothesised that E. marinus populations would present lower production and fitness, and higher intersexuality incidence with increasing anthropogenic pressure. According to a GAM model explaining ≈70% of the observed variability, E. marinus biomass depends on temperature, organic matter, Fucus area and time of the year. Significant differences were found between the gammarid biomass in Minho and Mondego estuaries and within sites from the same estuary. As expected, Ave estuary exhibited the lowest average annual production, abundance and fecundity rates. However, the highest average production was found in Mondego and not in Minho estuary, although the turnover ratio (P/B) of both estuaries was very similar. Besides the system’s global ecological status, E. marinus also seems to respond to microhabitat conditions, which may explain the spatial heterogeneity observed in the amphipod production within the same estuary. Intersexuality prevalence was negligible in the three populations, which does not support the idea of a link between anthropogenic pressure and intersexuality in E. marinus. We argue that the dependence of E. marinus on Fucus sp. should be further investigated to fully understand the role of both fucoids and the gammarid in coastal foodwebs.
The hydropeaking regime below hydropower facilities represents a serious threat to riverine fauna and may cause declines in populations living under its influence. However, the knowledge on direct fish responses to the threat of hydropeaking is limited. Here, we aimed to test whether the hydropeaking generated 12 km upstream may have a negative effect on the position of actively spawning rheophilic fish, asp, Leuciscus aspius. Two passive telemetry antenna arrays were used to record fish position on the spawning ground. We monitored the position of spawning fish (545, 764 and 852 individuals) in three one-month long spawning seasons in 2017–2019 and related the changes in detection probability on the two antenna arrays to flow conditions, temperature, time of a day and individual fish ID. The fish detection on the spawning ground was negatively affected by the flow change (both increase and decrease) in time. Moreover, the probability of fish detection was also influenced by water temperature, the time of the day and, as seen from the magnitude of individual random effect variability, the detection probability was rather individual-specific. Hydropeaking resulted in the change of spawning behaviour and likely caused interruption of spawning or shifting spawning outside the optimal area for egg development. We therefore advise to reduce the hydropeaking regime during the rheophilic fish spawning season under fisheries or conservation interests.

Fish communities differ significantly between the littoral and the pelagic habitats. This paper attempts to define the shift in communities between the two habitats based on the European standard gillnet catch. We sampled the benthic and pelagic habitats from shore to shore in Lake Most and Římov Reservoir (Czech Republic). The 3 m deep pelagic nets were spanned across the water body at equal distances from two boundary points, where the depth was 3.5 m. The benthic community contained more fish, more species, and smaller individuals. The mild sloped littoral with a soft bottom attracted more fish than the sloping bank with a hard bottom and less benthos and large Daphnia. The catch of the pelagic nets was dominated by eurytopic fish—rudd (Scardinius erythrophthalmus) and roach (Rutilus rutilus) in Most and bleak (Alburnus alburnus) in Římov. With the exception of one case where overgrown macrophytes extended the structured habitat, the largest shift from the benthic to the pelagic community was observed only in the first pelagic gillnet above the bottom depth of 3.5 m. Open water catches were relatively constant with small signs of decline towards the middle of the lake. The results indicate that the benthic gillnet catch is representative of a very limited area and volume, while most of the volume is dominated by the pelagic community. This has important consequences for the assessment of the community parameters of the whole lake following the European standards for gillnet sampling design.

Movement ecology is increasingly relying on experimental approaches and hypothesis testing to reveal how, when, where, why, and which animals move. Movement of megafauna is inherently interesting but many of the fundamental questions of movement ecology can be efficiently tested in study systems with high degrees of control. Lakes can be seen as microcosms for studying ecological processes and the use of high-resolution positioning systems to triangulate exact coordinates of fish, along with sensors that relay information about depth, temperature, acceleration, predation, and more, can be used to answer some of movement ecology’s most pressing questions. We describe how key questions in animal movement have been approached and how experiments can be designed to gather information about movement processes to answer questions about the physiological, genetic, and environmental drivers of movement using lakes. We submit that whole lake telemetry studies have a key role to play not only in movement ecology but more broadly in biology as key scientific arenas for knowledge advancement. New hardware for tracking aquatic animals and statistical tools for understanding the processes underlying detection data will continue to advance the potential for revealing the paradigms that govern movement and biological phenomena not just within lakes but in other realms spanning lands and oceans.

Many endangered fish species in the wild are artificially bred, and their populations are strengthened by the stocking of aquaculture-raised juveniles. Because fish from aquaculture are generally not well prepared for the challenging life in the wild, we tested whether training for selected challenges could improve fish survival after stocking. We chose conditioning on predation pressure (by learning predator image of northern pike Esox lucius using predator chemical cues and visual stimuli), increased rearing water velocity 20 cm × s−1, and direct exposure to predation. The juvenile cyprinid fish asp (Leuciscus aspius) was used as a model prey species. A total of 7949 asp were reared in four groups using a combination of high flow, predation, and control treatments (low flow, no predation; 2018, 2149, 1929, and 1856 individuals, respectively). Of these, 1800 individuals were released into three ponds with pike, and their mortality rates were monitored in relation to predation for two months after stocking using passive telemetry arrays. The remaining 6149 aquaculture-reared individuals were released directly into a large reservoir, while 1426 individuals that survived pike predation for two months were released after the pond experiment ended. Fish survival in a reservoir was monitored in 2020 and 2021 by boat electrofishing and passive telemetry. The effect of training in aquaculture was not detected in pond conditions, but the fish that survived direct predation from pike for two months in the semi-natural treatment were more likely to survive in the wild than their aquaculture-reared counterparts. In the laboratory environment, asp responded to predator chemical cues with an increase in shoal cohesion and swimming activity, which demonstrate their ability to detect chemical cues. However, exposure to more fluvial conditions did not result in increased critical swimming speed. The study suggests that conditioning tested in aquaculture may not be sufficient to prepare fish for the wild, while exposing fish to direct predation could increase fish survival.

The body condition of the shore crab Carcinus maenas in a temperate coastal system (western Dutch Wadden Sea) was followed over 14 mo. Fulton’s condition factor K, dry weight condition and the percentage of dry weight were determined as indirect indices, while bomb calorimetry was applied to obtain the energy density and total energy, as direct biochemical measures of condition. General linear models identified sex, size and season as relevant regressors explaining observed variance in crab condition, whereas colour morphotype effect was negligible. The seasonal pattern was consistent with the natural cycling in temperature and expected food availability, but the peak in body condition differed depending on the type of measure used: energy peaked in autumn, while morphometric condition was at its highest in winter, uncovering different latencies in the response of direct and indirect indices. Concordant with higher energy investment in reproduction, body condition and energy content of non-ovigerous females were higher than those of males, and egg-bearing females always had the lowest condition values. Energy content of adult females ranged from 16.37 ± 1.30 (winter 2013) to 19.83 ± 0.54 kJ g-1 ash-free dry weight (AFDW) (autumn 2013), attaining 18.77 ± 1.22 kJ g-1 AFDW prior to the onset of reproduction in 2012, while maximum energy density of ovigerous females (eggs excluded) was 16.49 ± 0.64 kJ g-1 AFDW. Besides low correlation between indirect and direct indices, fluctuations were more pronounced in the energetic data. Therefore, the morphometric measures seem weak surrogates to estimate energy density of these crabs.

Introduction Biological invasions are a major threat to global biodiversity and can have substantial socioeconomic costs. Although invasive non–native species have been studied extensively, their monitoring and management are often inadequate (Pergl et al. 2020). Moreover, the great harm invasive non–native species cause tends to be underestimated by the public and their management often opposed (Courchamp et al. 2017). There is a need to better understand societal awareness, perceptions, values, and attitudes toward invasive non–native species and the level of societal support for management plans. However, research to gauge these factors is rare and difficult to implement (Verbrugge et al. 2013; Lindemann–Matthies 2016). Conservation culturomics focuses on the study of human interactions with nature through the quantitative analysis of voluminous digital data to aid conservation (Ladle et al. 2016). It has great potential to inform invasion science and practice by providing new opportunities to gauge societal awareness and attitudes toward invasive non–native species. Digital data can also provide information on distributions, spread dynamic, life history, and impacts of invasive non–native species within the framework of iEcology (Jarić et al. 2020). iEcology is the study of ecological patterns and processes based on ecological data generated for other purposes and stored digitally. Culturomics and iEcology use similar data sources, but iEcology focuses on broad ecological patterns and processes, rather than human–nature interactions.
Using archived fish scale samples together with long-term monitoring data, this study investigates the potential of fish scales to record historical changes in the aquatic environment. We analysed stable carbon (δ¹³C) and nitrogen (δ¹⁵N) isotopes in the scales of two planktivorous cyprinid species collected from the meso-eutrophic Římov Reservoir, Czechia, over its entire four-decade history (1979–2016). The δ¹³C of the fish scales varied greatly throughout the reservoir history. The lowest δ¹³C values were observed immediately after the reservoir was filled in 1979, indicating that fish production at that time was likely partially supported by ¹³C-depleted CO2 released from the inundated soil. During the 1980s, due to the high levels of phytoplankton production stimulated by high phosphorus inputs from the catchment, the δ¹³C values substantially increased. However, since 1990, the δ¹³C values have generally decreased, reflecting a gradual reduction in reservoir primary production caused by the decreasing input of phosphorus and increasing input of dissolved organic carbon from the catchment. The δ¹³C of fish scales was also used to reconstruct the CO2 concentration of the surface water. The reconstructed CO2 varied significantly during the four-decade history, but it was always below the air-equilibrium concentration, suggesting that the surface water of the reservoir has consistently absorbed atmospheric carbon. The fish-scale δ¹⁵N values remained relatively stable, while slightly increasing within three years after impoundment, likely because the nitrogen supply was high throughout the studied period. Our study contributes to the growing body of literature demonstrating that stable isotope analysis of archived biological samples is a promising approach for understanding historical trends in the biogeochemistry of aquatic environments. In particular, our results highlight the potential of δ¹³C in archived fish scales in reconstructing carbon cycle changes and evaluating human impacts on aquatic ecosystems.

Human‐induced changes in the hydrological regimes of lotic waters such as hydropeaking have significant negative impacts on riverine life. However, the impacts of dynamic changes in water flow on adhesive fish eggs are not very well known. We focused on the effects of hydropeaking on the spawning ground of a rheophilic cyprinid fish, the asp (Leuciscus aspius). We tested whether a sudden increase in water velocity caused by hydropeaking may have negative effect on the adhesive eggs by the combination of field observations and laboratory experiments. The main objectives of the study were to: i) investigate abiotic characteristics of an asp spawning ground, ii) monitor egg densities in relation to hydropeaking events and iii) test detachment rates of the asp eggs in laboratory conditions in relation to water velocity. The asp spawning ground was associated with shallow water depths (0.2–0.4 m) and flowing water (0.1–0.4 m.s‐1) during base flow. The water velocity that occurred on the spawning ground during the hydropeaking event was measured to be from 0.7–1.2 m.s‐1. Asp eggs nearly disappeared from the spawning ground before their hatching time probably due to several hydropeaking events. The laboratory experiments showed the significant dependency of egg detachment rates on the water velocity and substrate type with a critical value of 0.7 m.s‐1. Our data suggested that eggs may be negatively impacted by flow alterations. Avoiding hydropeaking or keeping water velocity below critical values is recommended for the management of rheophilous fish spawning grounds.

High reproductive performance is the key attribute of male fitness, especially due to the high reproductive skew among the males of most animal species. Males of long-lived iteroparous species have opportunities to improve upon their previous reproductive attempts with increasing age. We collected individual-specific reproductive behaviour and age data on a cyprinid fish, the asp (Leuciscus aspius), from 2015 to 2019. We tested whether males changed their performance over time using a unique dataset where individual performance was recorded yearly with passive telemetry. Individual fish behaviour was tracked from one to five reproductive seasons at least a year after the tagging. Fish were scored by measures of quality (first arrival time, number of visits and time spent in the reproductive grounds, and encountered proportion of males to all adult fish). In general, fish improved in the first three metrics with age, suggesting a shift towards behaviours likely to enhance reproductive success as individuals aged. A larger size at tagging was predictive of earlier fish arrival on the spawning ground in subsequent years. Our study therefore demonstrates the importance of age as a factor when considering the potential reproductive success of long-lived fish species. High reproductive performance is the key attribute of male fitness. Males of long-lived species reproducing multiple times in their life have opportunities to improve upon their previous reproductive performance with increasing age. In this 5-year study, we tracked a large cyprinid fish with telemetry systems during their reproduction. We investigated the age-related behavioural changes in males and demonstrated the improvement of male reproductive timing and length of stay with potential repercussions for male’s reproductive output. We emphasize the importance of old and experienced individuals among the fish population, which are often targeted and selectively removed from the human-managed waters.
Fish stocking is one of the most widespread and frequent management strategies in freshwater systems. However, the contribution of stocked fish to the population is seldom investigated, and hence the effectiveness of this strategy is virtually unknown for many populations. Understanding the contribution of stocked fish into the population is crucial because it allows the disentanglement of the confounding effects generated by allochthonous individuals into the estimation of survival and growth rates of the population. To discriminate between the allochthonous and autochthonous individuals in a population, the shape of sagittae otoliths from pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) where compared. Results indicated significant differences among stocked and non-stocked fish, with the former having smaller and wider sagittae otoliths than the latter. Our results suggest that this technique can be used to discriminate the natal origin of fish in a much faster and cheaper way than commonly used techniques.

The ongoing digital revolution in the age of big data is opening new research opportunities. Culturomics and iEcology, two emerging research areas based on the analysis of online data resources, can provide novel scientific insights and inform conservation and management efforts. To date, culturomics and iEcology have been applied primarily in the terrestrial realm. Here, we advocate for expanding such applications to the aquatic realm by providing a brief overview of these new approaches and outlining key areas in which culturomics and iEcology are likely to have the highest impact, including the management of protected areas; fisheries; flagship species identification; detection and distribution of threatened, rare, and alien species; assessment of ecosystem status and anthropogenic impacts; and social impact assessment. When deployed in the right context with awareness of potential biases, culturomics and iEcology are ripe for rapid development as low-cost research approaches based on data available from digital sources, with increasingly diverse applications for aquatic ecosystems.
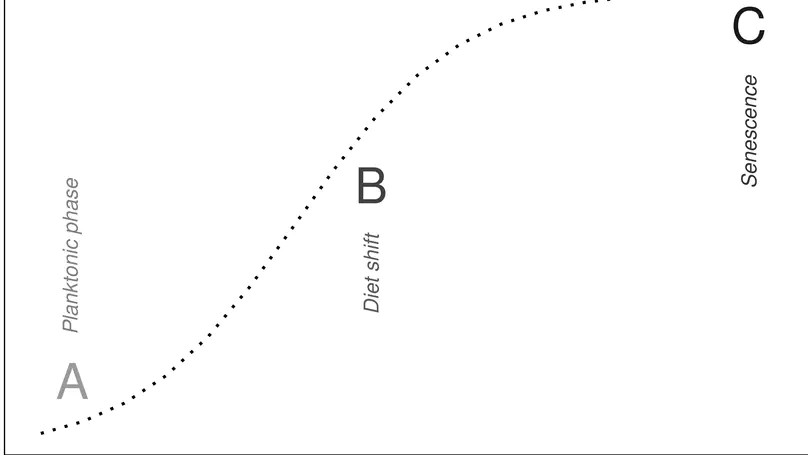
Fish otoliths are conservative structures that are widely used on fishery science for multiple purposes. Despite its relevance in the research field, little is known about the ontogeny and inter-population effects on the otolith of freshwater fish. In this study we used otoliths from 1800 European perch (Perca fluviatilis) individuals from 9 different populations to analyze the ontogenetic and inter-population differences on the otolith shape using six morphometric indices. The relationship between fish and otolith length was fitted using three different regression models (linear, power and logistic) to identify the best allometric relationship. Our results show that there are strong ontogenetic and interpopulation differences in P. fluviatilis otolith shapes. We also show that the relationship between the fish and otolith length follows a logistic curve. The ontogenetic differences on otolith shape might be related to extrinsic factors (diet shift and intra and interspecific competition) in each ecosystem, given that the reservoirs are different and no clear pattern on the otolith shapes can be distinguished among populations. Our results imply that the available back-calculation models may not always provide accurate estimates of P. fluviatilis length and that a model that takes into account the real allometric relationship for the species can improve the fish length estimations of back-calculated fish lengths for the European perch.

Digital data are accumulating at unprecedented rates. These contain a lot of information about the natural world, some of which can be used to answer key ecological questions. Here, we introduce iEcology (i.e., internet ecology), an emerging research approach that uses diverse online data sources and methods to generate insights about species distribution over space and time, interactions and dynamics of organisms and their environment, and anthropogenic impacts. We review iEcology data sources and methods, and provide examples of potential research applications. We also outline approaches to reduce potential biases and improve reliability and applicability. As technologies and expertise improve, and costs diminish, iEcology will become an increasingly important means to gain novel insights into the natural world.

Wildlife monitoring using passive telemetry has become a robust method for investigating animal migration. With increased use, this method progressively pollutes the environment with technological waste represented by so called ghost tags (PIT tags ending in the environment due to reproductive expulsions, shedding or animal mortality). However, their presence in the environment may lead to failed detections of living individuals. We used tagging data from studies of the asp Leuciscus aspius and the bleak Alburnus alburnus collected from 2014 to 2018 and located ghost tag positions on the monitored spawning site using portable backpack reader for their detection. We modelled virtual river-wide flat-bed antennas (widths 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 m) representing monitoring effort and estimated the probability of the presence of ghost tags within the antenna field. Of 3724 PIT tags used in the study, we detected on the spawning ground 173 ghost tags originating from long-term monitoring. The ghost tags accumulated in the environment in time, suggesting insufficient degradation rate or shift downstream from the research site. Number of ghost tags present on the spawning ground led to high probability of disabled readings of tagged fish passing through the antenna electro-magnetic field. We demonstrate how accumulated ghost tags may cause detection failures for focal species and incomplete data acquisition. We infer that intensive long-term monitoring using PIT tag technology may encumber future data acquisition or entail additional costs for clean-up.
Intraspecific agonistic interactions are widespread across the animal kingdom, with many individual morphological and physiological characteristics playing important roles in the fate of disputes. Additionally, changes to environmental conditions can influence the outcomes of animal contests. The shore crab (Carcinus maenas) is a globally distributed species, present in numerous coastal and estuarine temperate systems around the world. Although shore crabs are highly tolerant to changes in temperature, this parameter has important physiological effects on the species’ ecology, while its effects on behavior are not fully understood. Our study aims to investigate how different individual characteristics (such as sex, color morphotype, carapace and chela morphology) and temperature conditions affect the dyadic interactions between shore crabs when disputing food resources. In general, the differences in carapace width between opponents, their sexes, color morphotypes and the temperature conditions interacted and were important predictors of the contest fate. We found that the body size and color morphotype of C. maenas determined the fate of dyadic disputes. However, the higher temperatures disrupted the well-established dominance of the larger red color morphotype individuals. Overall, the agonistic contest results suggest higher plasticity than previously acknowledged.
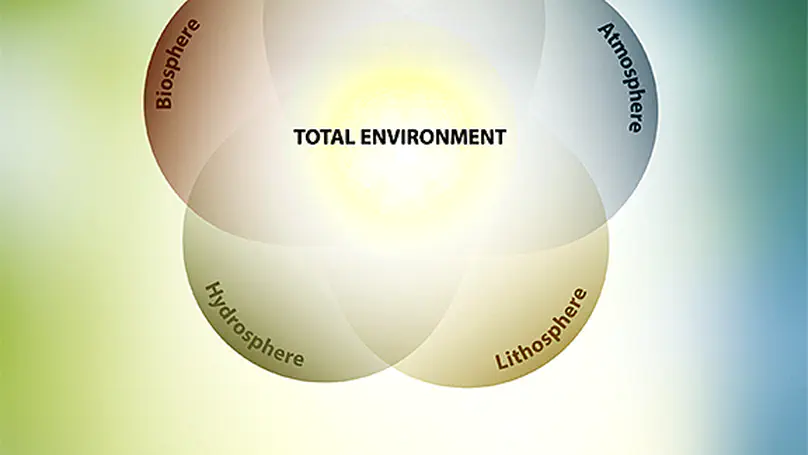
Bivalve shells can persist over a geological time, acting as important physical resources to the associated fauna. However, few studies have investigated their relevance as persistent long-term ecological attributes to the ecosystem. As such, it is relevant to investigate the shell decays in riverine systems subjected to different environmental conditions. Towards this end, shells of four bivalve species (Anodonta anatina, Corbicula fluminea, Potomida littoralis and Unio delphinus) were made available individually and in clusters of different sizes. The effects of river flow and seasonality were assessed by recording the decay rates of shells in lentic and lotic habitats throughout the year. Our results evidenced that the decays varied among species and depend on shell size, water flow and season. Thin shelled species (A. anatina and U. delphinus) showed the highest mean percentage of decay per month, 3.17% (lotic) and 2.77% (lotic), respectively, and thick shelled species (C. fluminea and P. littoralis) the lowest, 2.02% (lotic) and 1.83% (lotic), respectively. Size was a relevant variable explaining decays, with the smallest shells presenting the highest values, 1.2–2.0 times higher compared to the other size classes. Also, robustness showed to be the most relevant feature explaining the decays in thick shelled species. River flow was also a relevant descriptor of the decays, with higher decays observed in the lotic compared to the lentic habitats. Furthermore, lower decays were observed mainly during summer (lentic site), and autumn (lotic site) associated to the burial effect of leaves. In summary, shells of the native species A. anatina and U. delphinus are expected to persist and contribute less as habitat engineering species, than shells of the native P. littoralis and invasive C. fluminea species. This is especially valid to lotic habitats where the decays were up to 2.13 times higher than in lentic habitats.
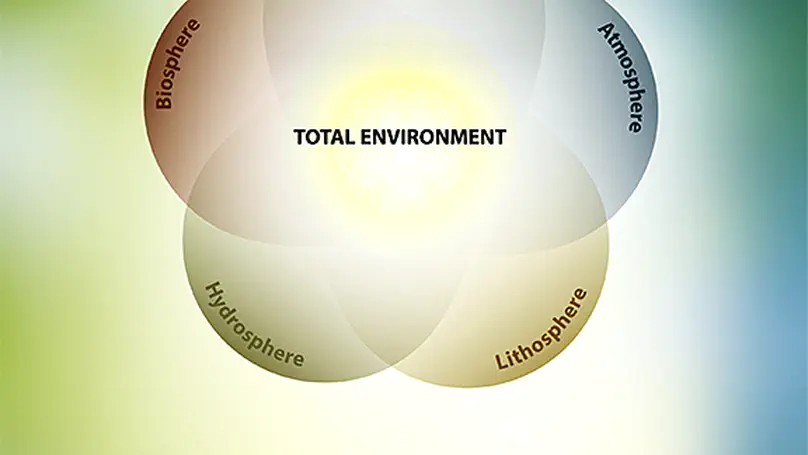
A population dynamics model was developed to assess the short and long-term effects of temperature and salinity variations in the common goby Pomatoschistus microps in a Portuguese estuary (Minho estuary, NW Portugal). The population was divided into juveniles, females and males, which constituted the model’s state variables. Linear regressions between the observed and the predicted density of juveniles, females and the total population were significant. Parameter’s sensitivity and uncertainty analysis were estimated. The model was able to satisfactory describe the P. microps population dynamics, and thus was used to simulate the effects of climatic changes on the fish population. Simulations indicated that the common goby population is sensitive to both temperature and salinity changes. Overall, scenarios of +4 °C increase caused significant population decreases. Similarly, increased salinities led to a population shrinkage, whereas scenarios of salinity decrease generated an opposite variation on the population. According to the IPCC predictions for climatic tendencies, the population of the common goby will tend to decrease in the near future, experiencing marked oscillations (decrease or increase) during climatic extremes, namely droughts and floods, respectively. These results may be a useful tool for future planning and management of estuarine systems given that the common goby is an important species of estuarine food webs in many temperate ecosystems.

Animals that do not provide parental care have to secure the survival of their offspring by ensuring a safe reproductive environment or smart timing tactics. Nocturnal spawning behaviour of many fish species is an example of the latter behaviour in the animal kingdom and is hypothesized to provide a survival advantage to the eggs spawned during the night. In order to test the efficiency of the smart timing tactics in a freshwater fish, a study was carried out of the interaction of the rheophilic spawner (asp Leuciscus aspius) and the predator of its drifting eggs (bleak Alburnus alburnus) using passive telemetry. According to a model based on acquired data, asp laid 63% of its eggs at night, while vision oriented bleak was present in 92% of the time during the day. This study gives support to the predator avoidance hypothesis, which expects animals to reproduce in a period when the probability of offspring predation is at its lowest.
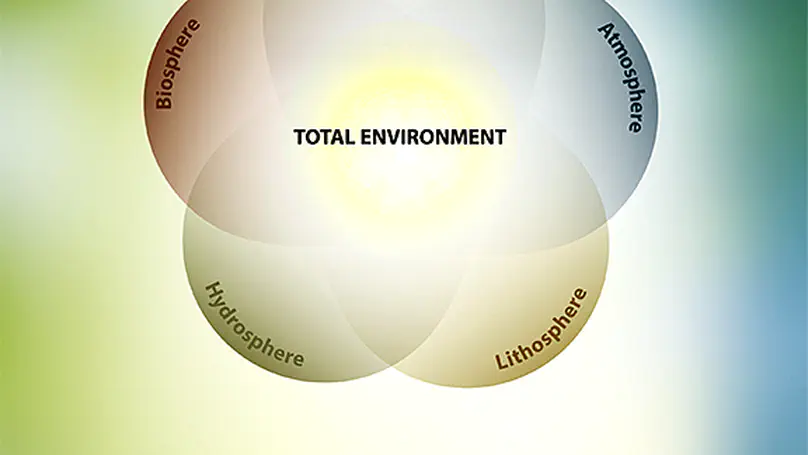
Bivalves may play a major role in structuring aquatic communities. This may be especially relevant in aquatic communities dominated by non-native invasive bivalves, which can contribute to the increase of habitat homogenization. In this study, we assess how habitat homogenization, through the reduction of empty bivalve shells identities, influences the macroinvertebrate assemblages. Towards this end, a manipulative experiment with the empty shells of two native (Potomida littoralis and Unio delphinus) and one non-native (Corbicula fluminea) species was performed. Seven treatments were prepared, three of them consisting of homogeneous substrates using shells of one species, and four of them consisting in heterogeneous substrates using more than one species. The associated fauna colonizing different treatments was analyzed through taxonomic and trait-based approaches. Our results showed that the substrate complexity influenced the density of macroinvertebrates, with the heterogeneous treatments significantly yielding more dense assemblages. Also, the trait patterns differed among the levels of habitat heterogeneity, influencing mainly organisms that feed on microphytes of both small and big sizes, that inhabit areas with slow to moderate water flow, and that have short and long live cycles. Further, the functional diversity was not influenced by the substrate heterogeneity. Therefore, the habitat homogenization, through the accumulation of non-native C. fluminea empty shells in the river bottom, did not affect the functional diversity of the macroinvertebrate assemblages.

The perception of danger represents an essential ability of prey for gaining an informational advantage over their natural enemies. Especially in complex environments or at night, animals strongly rely on chemoreception to avoid predators. The ability to recognize danger by chemical cues and subsequent adaptive responses to predation threats should generally increase prey survival. Recent findings suggest that European catfish (Silurus glanis) introduction induce changes in fish community and we tested whether the direction of change can be attributed to differences in chemical cue perception. We tested behavioral response to chemical cues using three species of freshwater fish common in European water: rudd (Scardinius erythrophthalmus), roach (Rutilus rutilus), and perch (Perca fluviatilis). Further, we conducted a prey selectivity experiment to evaluate the prey preferences of the European catfish. Roach exhibited the strongest reaction to chemical cues, rudd decreased use of refuge and perch did not alter any behavior in the experiment. These findings suggest that chemical cue perception might be behind community data change and we encourage collecting more community data of tested prey species before and after European catfish introduction to test the hypothesis. We conclude that used prey species can be used as a model species to verify whether chemical cue perception enhances prey survival.

Co-extinctions are increasingly recognized as one of the major processes leading to the global biodiversity crisis, but there is still limited scientific evidence on the magnitude of potential impacts and causal mechanisms responsible for the decline of affiliate (dependent) species. Freshwater mussels (Bivalvia, Unionida), one of the most threatened faunal groups on Earth, need to pass through a parasitic larval (glochidia) phase using fishes as hosts to complete their life cycle. Here, we provide a synthesis of published evidence on the fish–mussel relationship to explore possible patterns in co-extinction risk and discuss the main threats affecting this interaction. We retrieved 205 publications until December 2015, most of which were performed in North America, completed under laboratory conditions and were aimed at characterizing the life cycle and/or determining the suitable fish hosts for freshwater mussels. Mussel species were reported to infest between one and 53 fish species, with some fish families (e.g., Cyprinidae and Percidae) being used more often as hosts than others. No relationship was found between the breadth of host use and the extinction risk of freshwater mussels. Very few studies focused on threats affecting the fish–mussel relationship, a knowledge gap that may impair the application of future conservation measures. Here, we identify a variety of threats that may negatively affect fish species, document and discuss the concomitant impacts on freshwater mussels, and suggest directions for future studies.

Marine protected areas (MPAs) are important tools for the evaluation of the biodiversity and status of marine systems. However, not all MPAs are equal in their design and management; therefore, it is important to understand how different levels of protection affect the fish communities. In the present study, the shallow reef-area fishes of seven areas in Fernando de Noronha archipelago (north-eastern Brazil) with dissimilar habitat characteristics and different levels of environmental protection (no-take MPA and MPA) were compared. In total, 140 visual censuses were performed, in which 12 958 fishes of 27 families and 50 species were recorded. Differences were recorded between no-take MPAs and MPAs in the benthic composition, abiotic data and fish-community structure and composition. These differences were associated with a higher diversity, richness, density of larger fishes and top target fish families, and biomass per census (nearly 2-fold higher in the no-take MPA). Our findings suggested that the differences in the ichthyofauna were probably more related to the different levels of protection than to dissimilarities in the habitat structure among areas, and that the local no-take MPA (National Marine Park of Fernando de Noronha) is effective in maintaining the shallow reef-area fish communities healthy and diverse.
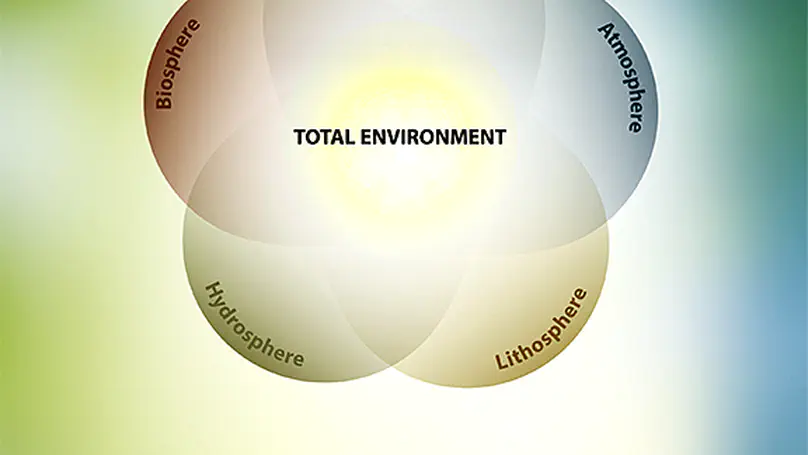
The Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) is well recognized for its invasive behavior and high ecological and economic impacts, being classified as one of the 100 worst invasive alien species (IAS) in Europe. In this study, we performed a manipulative experiment under natural conditions to assess the effects of C. fluminea on sediments biochemistry and on the structure of an estuarine microbial (fungi and bacteria) community. We placed 5 treatments (control, rock, closed, live and open) for 2 months in the Minho estuary (NW Iberian Peninsula). No differences were detected between treatments regarding the values of carbon (C), nitrite (NO2−), ammonium (NH4+), phosphate (PO43 −) and calcium (Ca) in the sediments; however, potassium (K) had higher values in the open treatment. Furthermore, we found that the presence of live C. fluminea stimulated fungal biomass (but not diversity) and bacterial diversity. Bioturbation activities by C. fluminea are possibly the main mechanism explaining these results; however, other factors such as the presence of other macroinvertebrate species and/or production of feces and pseudofeces by C. fluminea cannot be excluded. To our knowledge, this is the first manipulative experiment under natural conditions that clearly shows the effects of C. fluminea on an estuarine microbial community. Given the widespread distribution of this IAS and the paucity of quantitative assessments of invasive bivalves’ effects on microbial communities, it will be important that future studies further investigate these processes.
Resource pulses are episodes of low frequency, large magnitude and short duration that result in increased resource availability in space and time, with consequences for food web dynamics. Studies assessing the importance of resource pulses by invasive alien species in the interface between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems are rare, especially those in the direction from water to land. This study assessed the importance of massive die-offs of the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) as a resource pulse to the terrestrial invertebrate community after an extreme climatic event using a manipulative experiment. We used 5 levels of C. fluminea density (0, 100, 500, 1000 and 2000 ind·m− 2), with terrestrial invertebrates being censused 7, 30 and 90 days after C. fluminea addition. We also assessed the possible effect of plots position, where plots that delimited the experiment were assigned as edge plots and the remaining as core plots. Clear differences were detected in abundance, biomass, richness and diversity of terrestrial invertebrates depending on the C. fluminea density, time and position. Interestingly, the highest abundance of adult Diptera was observed 7 days after C. fluminea addition, whereas that of the other terrestrial invertebrates was on day 30, both with C. fluminea densities higher than 500 ind·m− 2 located on the edge of the experimental design. This study highlights the importance of major resource pulses after massive die-offs of invasive bivalves, contributing with remarkable amounts of carrion for adjacent terrestrial systems. Part of this carrion can be consumed directly by a great number of invertebrate species while the remainder can enter the detrital food web. Given the high density and biomass attained by several invasive bivalves worldwide and the predicted increase in the number, intensity and magnitude of extreme climatic events, the ecological importance of this phenomenon should be further investigated.

The Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) has been recognized as one of the most important invasive alien species in aquatic ecosystems and may have significant ecological and economic impacts. Recently, the presence of C. fluminea was associated with changes in benthic and epibenthic fauna. In this study, we aimed to understand the mechanisms underlying the effects of C. fluminea on an estuarine macrozoobenthic assemblage using a manipulative experiment. We used 5 different treatments (control, rock, closed, live, open), which were placed in a low sandy intertidal soft bottom area in the Minho estuary (NW Iberian Peninsula) for 2 months. We found that the presence of live and open empty shells of C. fluminea had positive effects on the density, biomass and species richness of macrozoobenthos, specifically on species belonging to Annelida, Mollusca and Crustacea. Our results may be explained by 2 main mechanisms: (1) the production of feces and pseudofeces by C. fluminea, which increases organic matter content and food resources for some macrozoobenthic species; and (2) ecosystem engineering activities by C. fluminea, which can create conditions for the establishment of other species via shell production and bioturbation in the sediments.

Freshwater flow regimes are particularly vulnerable to global climate change with changes to the volume and regime of water contributing to global declines in freshwater biodiversity. Droughts or floods can cause massive mortalities of freshwater bivalves, facilitating the accumulation of shells in the aquatic but also in adjacent terrestrial habitats. In order to fully understand the long term impact of these massive mortality events, it is important to assess how bivalve shells persist in the environment. Given that, the present study aimed at studying the shell decays of four different bivalve species (Anodonta anatina, Corbicula fluminea, Potomida littoralis and Unio delphinus) in aquatic (i.e. river) versus terrestrial (i.e. sand soil) habitats. Shell decay rates were significantly different among species and habitats. In the aquatic habitat the shell decay rates varied among species, with the native species A. anatina, which have the largest and thinnest shell, showing the highest decay rate. Alternatively, in the terrestrial habitat the shell decay rates were more even among species and not related to a particular shell feature or morphology, with the native U. delphinus showing the fastest decay. The shell decay rates were 6 to 12 times higher in aquatic than in the terrestrial habitat. These results suggest that bivalve shells can persist for long periods of time on both habitats (but mainly in terrestrial), which may perhaps trigger significant changes on the ecosystem structure and functioning.

Bivalve shells can potentially alter the structure of aquatic benthic communities. However, little is known about the effect that different shell morphologies have on their associated fauna. This study aimed to understand how empty shells, from four different freshwater bivalve species, affect macrozoobenthic communities, using the River Minho (Iberian Peninsula) as a study area. Three native (Anodonta anatina, Potomida littoralis, Unio delphinus) and one non-indigenous (Corbicula fluminea) species were used for this research. Comparisons among species and between scenarios (i.e. before and after invasion by C. fluminea) were performed. Our results suggest that macrozoobenthic community structure did not vary among treatments, with the exception of species richness, which was higher on shells of native species. Furthermore, little difference was detected when comparing scenarios with and without C. fluminea shells, despite dissimilarities in size and morphology between species. The empty shells of C. fluminea partially (in terms of density and biomass, but not in species richness) replaced the role of empty shells of native species as a physical substratum for the associated macrozoobenthic community.

Estuaries are highly productive and heterogeneous ecosystems, and hence they provide an excellent opportunity to study the population structure and feeding patterns of euryhaline species like the sand goby Pomatoschistus minutus. In this context the population dynamics of the sand goby was investigated during 18 months in the Minho estuary (NW Iberian Peninsula). The fish density varied significantly among estuarine areas and seasons, with most of the individuals being caught near the river mouth during the autumn (38 % of the total). Males, females and juveniles were not spatially segregated, as well as fishes belonging to different size classes. The sand goby fed mostly on crustaceans (Frequency of Occurrence - FO) = 35 %; Relative Abundance - RA = 40 %), detritus (FO = 27 %; RA = 23 %) and annelids (FO = 15 %; RA = 14 %), with no obvious difference between the diet of males and females. The density (up to 20 times) and the secondary production (up to 16 times) of the sand goby were substantially higher than in other southern European estuaries. Our results highlighted that the population dynamics of the sand goby can vary considerably among nearby systems and that the Minho estuary, probably due to the lower temperature and salinity values and also the different water circulation regime found in this system when compared to other Iberian estuaries, promotes noticeable differences on the P. minutus population dynamics.

This study aimed at comparing the feeding, territorial and agonistic behavior of the Rocas Gregory Stegastes rocasensis when guarding egg clutches. This was accomplished through underwater observations of 80 S. rocasensis individuals observed in four sampling sites in the Fernando de Noronha archipelago (SW Atlantic). Several differences were detected in the behavior of S. rocasensis, such as the reduced size of the territory, the feeding preferences and the aggressiveness towards intruders. Males guarding eggs defended territories twice as small as the ones that did not present egg clutches inside their territories. Additionally, they fed mostly on turf algae, while individuals without eggs in their territories fed mostly on turf and macroalgae. Fish guarding egg clutches elicited agonistic reactions mainly towards planktivores and omnivorous fishes, which could potentially prey on their eggs, while individuals without eggs clutches in their territories elicited agonistic reactions mainly towards herbivorous fishes. The results of the present study reinforces that damselfishes are able to identify the intruder’s identity and elicit agonistic reactions only toward species that may represent a threat to their eggs and/or farmed algae.

The common goby, Pomatoschistus microps, is a relevant species from estuarine food webs, playing important roles as predator of polychaetes and crustaceans and as prey for larger fishes and crustaceans. The Minho estuary (NW Portugal) is a relatively well preserved and productive system. To assess the population structure and production of P. microps in this estuary, monthly samples were undertaken in three different areas along an estuarine gradient in the lower estuary. The density of P. microps varied considerably among seasons and sampling stations, with higher densities occurring in summer and autumn. The lowest densities were found closer to the sea. In general, the density of females was higher than the density of males in all sampling stations, while juveniles were more abundant within a salt marsh area. Compared with other European estuaries, our data showed a remarkable higher density and production values of P. microps. This may be related to the high freshwater input and the low salinities found in this estuary. In addition, we hypothesize that the lower density of the sympatric species P. minutus and the high availability of bivalve shells observed in the Minho estuary may have also contributed to the present results, once P. minutus and P. microps often display a diet overlap and the bivalve shells are crucial for the common goby reproduction.

One of the most widespread invasive alien species (IAS) in aquatic ecosystems is the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. Several studies have shown that C. fluminea can cause large-scale changes in macrozoobenthic assemblages; however, very few attempted to investigate the effects of this IAS on mobile epibenthic species, such as fishes and crustaceans. In this context, the influence of C. fluminea on epibenthic species was investigated during one year by comparing the associated epibenthic fauna in three nearby sites of the Minho estuary (NW of the Iberian Peninsula), wherein the abiotic conditions are similar but the density of the Asian clam is highly different. From a total of 13 species, six were significantly influenced by C. fluminea; five responded positively, namely the brown shrimp Crangon crangon, the European eel Anguilla anguilla, the common goby Pomatoschistus microps, the brown trout Salmo trutta fario and the great pipefish Syngnathus acus, whereas the shore crab Carcinus maenas was negatively influenced. However, stomach contents analysis revealed that fish and crustacean species do not feed on C. fluminea, suggesting that this IAS is still not a large component of the diet of higher trophic levels in this estuarine ecosystem. Our results suggest that the structure provided by C. fluminea shells is likely to be one of the main factors responsible for the differences observed. C. fluminea physical structure seems to influence the epibenthic associated fauna, when found in densities higher than 1000 ind./m2, with sedentary small-bodied crustaceans and fishes being mainly attracted by the increasing in habitat complexity and consequent enhancement of heterogeneity and shelter availability.

The European flounder Platichthys flesus is a widely distributed epibenthic species and an important component of demersal fish assemblages in the European Atlantic coastal waters. In Portuguese estuaries, this species reaches high densities, especially in Minho estuary (NW Iberian Peninsula, Europe), potentially playing an important role in the system’s ecology. In this context, the population structure, production and the habitat use of juvenile P. flesus were investigated. Sampling took place monthly, from February 2009 until July 2010 along the entire estuarine gradient (5 sampling stations distributed in the first 29 km from the river mouth, with S1 located near the river mouth, S2 inside a salt marsh, S3 in a salinity transition zone, while S4 and S5 were located in the upper estuary). Flounder’s density varied significantly among sampling stations and seasons (two-way PERMANOVA: p < 0.001), with the majority of the individuals being found during the spring (30.1%) and in S3 and S4 (72.6%). Males and females presented an even distribution, with a higher proportion of males observed during summer. Fish length also differed among sampling stations and seasons (two-way PERMANOVA: p < 0.001), with larger fishes being found in S1 during the autumn (168.50 ± 59.50 mm) and the smallest in S4 during the spring (33.80 ± 3.12 mm). Size classes associated differently with environmental variables, with larger juveniles being more abundant in the downstream areas of the estuary, whereas smaller juveniles were related to higher water temperatures, suggesting a habitat segregation of P. flesus of different sizes. The fish condition of P. flesus in Minho estuary was higher than in other systems, probably due to the dominance of juveniles on the population. Also, the densities found in this estuary were up to 32 times higher than in other locations, suggesting that Minho estuary is an important nursery area for the species. The estimated secondary production of P. flesus was lower than previous studies acknowledged in the system (0.037 g.WWm− 2.year− 1), indicating that the production estimates of this species in estuaries can vary considerably depending on of several factors such as the sampling year and strategy, population and fish size.
This study aimed to assess the feeding association between coral reef fishes and the hydrozoan Millepora spp. in two different reef systems (Tamandaré reefs and Fernando de Noronha archipelago) of Pernambuco State (north-eastern Brazil). A total of eight reef fish species, predominantly juveniles, were recorded feeding on colonies of Millepora spp. during 35 records. The highest recorded feeding rate was 1.72 ± 0.87 bites.minute-1 for Sparisoma axillare and the lowest was 0.18 ± 0.40 bites.minute-1 for Stegastes rocasensis. The colony structure of the genus Millepora supports a high diversity of microfaunal and macrofaunal invertebrates, which may result in the frequent foraging behaviour observed here.
Reef fish usually display a remarkable variety of colours and coloration patterns. The colour patterns are largely used for species identification, and some morphologically conservative genera are highly dependent on coloration for this purpose. In this context, this paper aims to briefly describe unusual colour patterns recorded for territorial damselfish of the genus Stegastes in the south-western Atlantic Ocean. Four unreported coloration pattern types were observed in three species (S. fuscus, S. rocasensis and S. pictus). The pale morph which is characterized by individuals presenting whitish marks over the regular coloration pattern was recorded in S. fuscus in north-eastern reefs and S. rocasensis in Fernando de Noronha archipelago. On the other hand, S. fuscus and S. pictus presented other types of unusual coloration patterns, which are characterized by an irregular cover (blue or dusky) over the regular colour pattern. Another type of unusual coloration pattern was recorded for S. fuscus, which presented a yellowish/reddish dorso-anterior band. Additionally, two distinct colour patterns of adult S. variabilis, from the south-eastern and north-eastern Brazilian reefs are reported.

The present study compared the carapace structure of Carcinus maenas in two nearby sites (2 km apart) within Minho estuary, submitted to different physicochemical and ecological conditions (water temperature, pH, crabs’ density and sex ratio). The carapace structure of the carapace and chelae of the crabs presented significant differences between sampling sites (t-test; p < 0.01). The SIMPER analysis revealed that the Weight/CW and Thickness/CW ratios explained all the dissimilarities found among sites. Overall, the male carapace was proportionally thicker at station 2 (t-test; p < 0.01), while the female carapace was proportionally thicker at station 1 (t-test; p < 0.001). A thicker carapace can be advantageous when competing for food or a sexual partner. We hypothetized that, since at station 2, the density of individuals was twice higher than at station 1, it is likely that agonistic encounters are more frequent, thus favouring a thicker carapace.

Extirpation or even extinction of freshwater invertebrate species is a neglected conservation issue; declines in abundance and spatial distribution for freshwater invertebrates are far less documented than for vertebrate species. In the Minho River tidal freshwater wetlands (northwest of Iberian Peninsula), a rapid decline in density and biomass of the bivalve Pisidium amnicum was recorded at 16 different sites over seven years, from 2004 to 2010, without any sign of a potential recovery. Mean density values reached more than 80 ind.m−2 in 2004, but declined to less than 1 ind.m−2 in 2009 and 2010. An identical declining trend was observed for biomass. A significant reduction in the spatial distribution also occurred. The abiotic changes resulting from the 2005 heat wave and possibly the negative interactions imposed by the non-indigenous invasive bivalve Corbicula fluminea were the main factors responsible for the declining trends. Given the very low density, P. amnicum is facing a serious risk of extirpation in this ecosystem and conservational measures are urgently needed.

This paper presents the results of the first field study of the Brazilian endemic damselfish Stegastes rocasensis. Underwater data were collected at the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago (NE Brazil), where four sites were visually assayed for local territorial and feeding behaviors, as well as habitat use. S. rocasensis preferentially fed on turf and macroalgae, and during the afternoon period. Its territory size ranged from 0.26 to 13.86 m2 (1.61 ± 0.23 m2). Our findings suggest that adults preferably inhabit shallow, turf-rich areas, while sub-adults and juveniles occupy deeper areas with higher percent cover of invertebrates and hard corals, respectively. With regards to agonistic behaviors, pursuit of intruders was the most frequent reaction recorded (p < 0.001); the highest level of aggression was elicited by territorial herbivores (p < 0.001). Nevertheless, analysis of attacks elicited by different fish species within S. rocasensis’ territory showed that more attacks were launched on conspecifics than on other fish species.

Spatial distribution, microhabitat use and territorial and feeding behaviours were compared between the juveniles of two sympatric territorial damselfishes Stegastes variabilis and Stegastes fuscus on a small tropical reef in the south-western Atlantic Ocean. Juvenile S. variabilis were most abundant at sites subject to stronger hydrodynamics and with mixed benthic cover, whereas juvenile S. fuscus were most abundant at sheltered sites with dense turf algae cover. No differences regarding feeding habits were detected, with both species preferentially feeding on turf algae. Also, despite similarities in territory area and agonistic encounter rates, the identity and proportion of intruders involved in agonistic interactions differed significantly between species. These interdependent traits suggest strong asymmetric competition, with juvenile S. fuscus dominating high-quality sites and evicting juvenile S. variabilis to low quality, marginal areas of the reef.

Habitat use and the processes which determine fish distribution were evaluated at the reef flat and reef crest zones of a tropical, algal-dominated reef. Our comparisons indicated significant differences in the majority of the evaluated environmental characteristics between zones. Also, significant differences in the abundances of twelve, from thirteen analyzed species, were observed within and between-sites. According to null models, non-random patterns of species co-occurrences were significant, suggesting that fish guilds in both zones were non-randomly structured. Unexpectedly, structural complexity negatively affected overall species richness, but had a major positive influence on highly site-attached species such as a damselfish. Depth and substrate composition, particularly macroalgae cover, were positive determinants for the fish assemblage structure in the studied reef, prevailing over factors such as structural complexity and live coral cover. Our results are conflicting with other studies carried out in coral-dominated reefs of the Caribbean and Pacific, therefore supporting the idea that the factors which may potentially influence reef fish composition are highly site-dependent and variable.

The effects of tourist visitation and food provisioning on fish assemblages were assessed by visual censuses (stationary technique) carried out in a tropical reef in Northeastern Brazil. Comparisons of species abundance, richness, equitability, and trophic structure in the presence (PT) and absence (AT) of tourists suggest that tourist visitation and supplementary food influenced the structure of the fish assemblage, as follows: (a) diversity, equitability and species richness were significantly higher on the AT period, while the abundance of a particular species was significantly higher during PT; (b) trophic structure differed between the AT and PT periods, omnivores being more abundant during the latter period, while mobile invertivores, piscivores, roving herbivores and territorial herbivores were significantly more abundant on AT. Reef tourism is increasingly being regarded as an alternative to generate income for human coastal communities in the tropics. Therefore, closer examination of the consequences of the various components of this activity to reef system is a necessary step to assist conservation and management initiatives.
Associations of the hairy blenny Labrisomus nuchipinnis (Labrisomidae) are described for the first time from different observations made on the coast of Brazil, South Atlantic. The first involved a majid crab cleaning the fish and the second, another fish following closely a foraging hermit crab of the genus Paguristes (Diogenidae).

Shallow reefs on the northeastern coast of Brazil are rich, productive and diverse environments, with great ecological and economical importance. Picaozinho is located 1,500 m off the coast of Joao Pessoa city, Paraiba state, NE Brazil. The aim of this work is to provide an updated list of the reef fishes of Picaozinho, based on a survey of approximately 350 hours of direct observation using free dive techniques, and complemented by collection data and other unpublished records. A total of 102 species of 43 families were recorded. Of these, 36 are new occurrences for the reef and seven are species that have been recently resurrected from synonymy, mainly with Caribbean species previously cited for Brazil.

Uncontrolled recreational activities are known to cause severe damage to reef dwelling organisms and to the reef overall structure. In order to investigate the effects of human recreational activities on the reef fish assemblage, surveys were undertaken in two shallow coastal reefs (Picãozinho and Quebra Quilhas) with similar physiographic features. However, recreational activities only take place at the former, and the latter was investigated as a control reef. The most speciose and abundant families on both reefs were Pomacentridae, Scaridae, Haemulidae, Acanthuridae and Labridae, but species evenness was fairly different between the reefs due in particular to the extremely high abundance of the sergeant major Abudefduf saxatilis at Picãozinho. This species represented almost ⅔ of all individuals recorded at Picãozinho and was the underlying feature responsible for the assemblage structure pattern observed on this reef. The present study showed that one single species was of major influence on species evenness and trophic structure, and that unregulated recreational activities have the potential to severely alter reef fish assemblage structure.